The animal cell is absolutely incredible, with numerous organelles enclosed within the plasma membrane that perform specific functions. Besides the major functions of the nucleus and mitochondria, other organelles like ribosomes and lysosomes also contribute to important cellular activities. Let’s talk about lysosomes and ribosomes in detail.
What are Ribosomes?
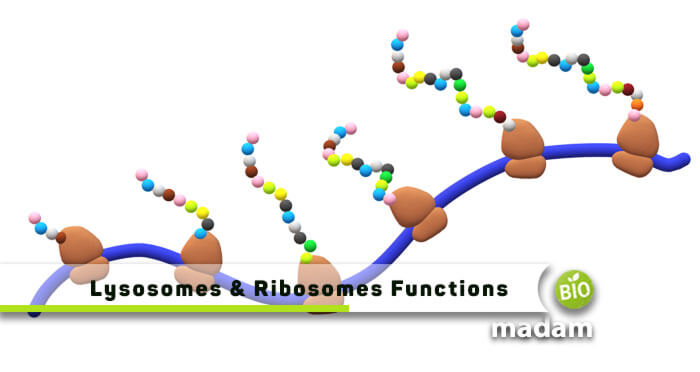
Ribosomes are present in different eukaryotic cells and are known as protein factories. They are freely floating in the cytosol or cytoplasm, while some are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are found in large quantities, and as many as 10 million ribosomes may be present in a human or animal cell.
Structure of Ribosomes
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits that join together to work and translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain for protein synthesis. The size of ribosomes differs in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, with eukaryotic ribosomes being larger. The smaller subunit is the site for mRNA binding, whereas the larger side is the site for amino acids.
The prokaryotic ribosomes are 200 Å in diameter and composed of two subunits (the 30S and 50S), making 70S for the entire organelle. Alternatively, the eukaryotic ribosome is the 80S, made of one 40S and one 60S with a diameter of 300 Å.
Ribosomes are primarily composed of a specific type of RNA and proteins in equal amounts that constitute the subunits.
37% to 62% of the ribosome composition is RNA, and the rest of it is made of proteins. All the ribosomes have a similar central structure that is alike in all despite the size difference in different cells. Yet, the RNA is arranged in varying tertiary structures. Bigger ribosomes have RNA in the form of numerous continuous infusions.
Function of Ribosomes
Ribosomes are the primary site of protein synthesis. Proteins are the body’s building blocks and contribute to cell generation and repair besides directing chemical processes. Ribosomes also help transform hereditary information from mRNA to proteins during DNA translation.
What are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are known as suicide bags as they ingest biomolecules and degrade them. They are one of the vital cell organelles as they help the cells get rid of unwanted substances. They are absent in prokaryotic and plant cells and present in eukaryotic animal cells.
Lysosomes are sac-shaped that contain hydrolytic enzymes to break down biomolecules to eliminate them from the body.
Structure of Lysosomes
Lysosomes are simple cell organelles with a straightforward structure. They have a sac made of a single membrane that contains enzyme complexes within the lumen. Apart from the breakdown of debris and other biological polymers, they also regulate energy metabolism, restore plasma membranes, and count discharged material. They are usually 0.1 μm and 0.6 μm in size up to 1.2 μm.
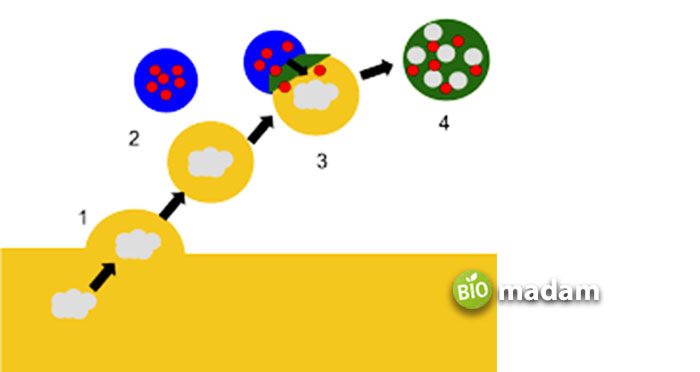
Function of Lysosomes
Though the main function of Lysosomes is the breakdown of debris in the cell, they also assist in the removal of waste. Lysosomes, by creating a vacuole, ingest the cellular debris inside themselves through endocytosis. They also facilitate the restoration of the plasma membrane and cell signaling besides getting rid of water material through endocytosis and autophagy.
FAQs
Do plant cells have lysosomes?
Plant cells do not have lysosomes like animal cells, but the vacuoles help remove materials from the cell. They function exactly as a lysosome for animal cells.
Where are hydrolytic enzymes manufactured?
Hydrolytic enzymes are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum that reaches lysosomes from the Golgi apparatus.
Can cells function without ribosomes?
Eukaryotic organisms, especially animals and humans, have protein as the main building unit. As ribosomes are the protein synthesis factories, they are crucial for the sustenance of life.
The Bottom Line
Lysosomes and ribosomes are essential to body organelles that perform different functions. Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis, whereas lysosomes remove debris from the cell. The function of lysosomes and ribosomes is inevitable, and animal bodies would not be able to develop properly if any one of them is absent.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.