The human body comprises various anatomical and physiological features that work together to produce action. The nervous system is one of the most critical functions in the human body. Components of the nervous system, including the somatic and autonomic nervous systems, collectively perform vital roles by transmitting signals. The nervous system transmits signals to and from the brain using neurons. The neurons comprise different parts, including the axon. Let’s tell you more about neurons and the function of the axon terminal.
What is the Axon Terminal?
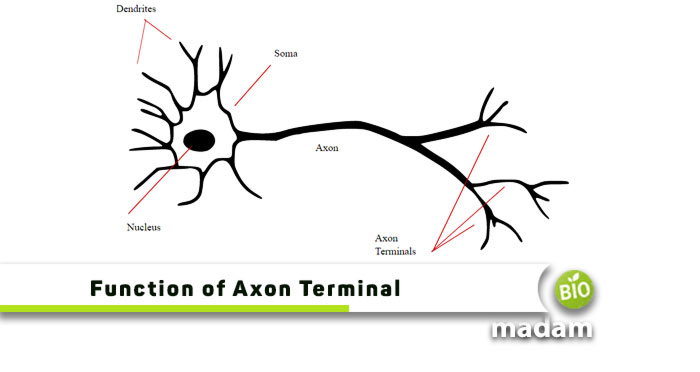
Before we talk about the function of the axon terminal, it is important to understand what the axon terminal is. The axon terminal is one of the main parts of the neuron. The neuron comprises cell body, cell membrane, dendrites, axon, axon hillock, and axon terminal.
The axon terminal is defined as “the terminal or end part of the axon that releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap near another neuron or gland in the body.”
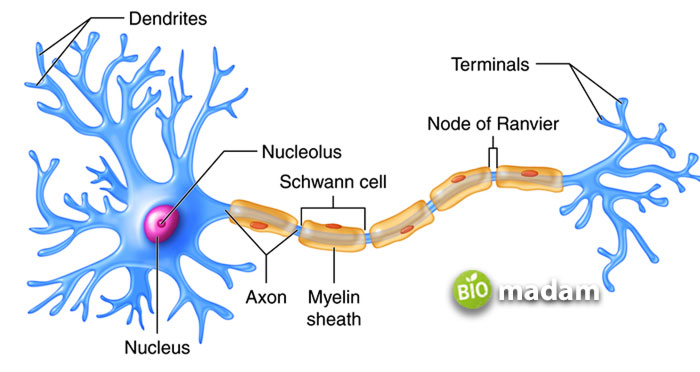
Axon terminals are present at the end of every neuron and thus are found at every synapse throughout the body. They are typically branched and club-like in appearance and enlarged compared to the structure of the rest of the axon. The output receptors send information to the other neuron, where the dendrites act as the input receptors and receive the information.
These terminals also contain synaptic vesicles having neurotransmitters that float around in these terminals before activation.
Function of Axon Terminal
The main function of axon terminals is the communication between neurons by transmitting signals to the dendrites of the other neuron across the synaptic gap. The synaptic gap transfers information from the efferent to the afferent nerves.
When the central nervous system sends a signal, it gives rise to a chain reaction where the impulses are transferred to the next neuron. The neurotransmitters in the axon terminals are unactivated unless an action potential initiates the process. The action potential occurs through the inwards movement of sodium and the outward movement of potassium.
The action potential generates a voltage difference between the external and internal environment across the cell membrane. The neurotransmitters initiate an action potential when they make contact with each other. When the potential action moves to the neuron, it pushes the neuron to access free-floating calcium ions, which take place through electrical depolarization.
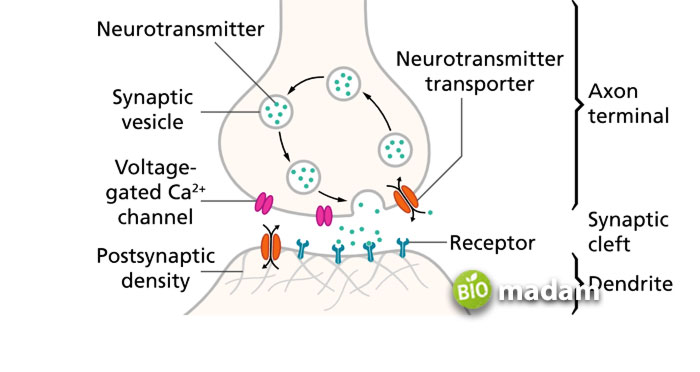
The calcium ions enable the fusion of vesicles with the axon terminal’s membrane, besides the formation of fusion pores by several types of proteins. Thus, the neurotransmitters can pass through the pores within the synaptic vesicles.
The neurotransmitters pass through these pores and reach their targeted cells. The movement of neurotransmitters between neurons initiates binding to the receptor on the other neuron. The neuron then creates an action potential to trigger the information transfer process.
Then, the axon terminals allow the passage of information across neurons through neurotransmitters. This process takes place within a short time, after which the neurotransmitters reabsorb or are broken down by various enzymes.
What if the Axon Terminal does not Function Properly?
As the main function of the axon is to transfer information across the synaptic gap, malfunctioning the axon terminal can restrict the process. The inability of the axon terminal to pass information to the next neuron also impacts the organism’s ability to carry out biological functions. The transfer of neurotransmitters across the nervous system facilitates muscular and skeletal movements as well. So, loss of functionality in the axon terminal can lead to paralysis, injury, or even death.
The Bottom Line
Neurons, like sensory and motor neurons, are critical to the normal functioning of the body as they carry signals from body parts to the signals. The brain then sends these signals to the effector organ to perform a specific function. Neurons comprise axons and axon terminals that carry the information to the next neuron through the synaptic gap. The axon terminals transmit the signals to the dendrites of the other neuron to initiate a chain reaction vital for many functions within the body.
FAQs
What are the types of axon terminals?
Axon terminals on the end of neurons perform the same function but might differ in size from dense, large, and medium-sized.
What is the function of the axon hillock in a neuron?
The axon hillock is the potential-generating region of the neuron where electrical nerve activity occurs that determines the possibility of an action potential.
How many axon terminals are there?
The number of axon terminals in a neuron is not confined or equal in all. Some neurons may have one axon terminal, while others have multiple terminals.
What is the function of synapse?
Synapses occur between two neurons and connect sensory organs in the peripheral nervous system to the brain. They connect the neurons in the brain and the rest of the body.
Do axon terminals have ribosomes?
Recent research has shown the presence of ribosomes to perform particular function in the initial axon segment and along the axon shaft than only at the ends.
Are axon terminals made of myelin?
The axons in neurons may or may not have myelin sheath covering their surface. The membrane has a high lipid-to-protein ratio in the peripheral nervous system.
Do axon terminals contain acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter present throughout the neurons and their synapses. The highest concentration of acetylcholine is in axon terminals.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.