Recently updated on March 17th, 2023 at 09:09 am
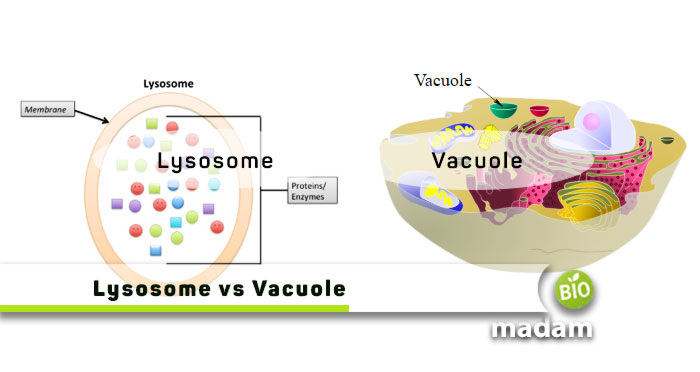
Almost all eukaryotic cells contain essential organelles, like lysosomes and vacuoles, besides plasma membrane, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc. Lysosomes and Vacuoles are especially involved in the storage and breakdown of materials. Both are vesicles that perform specific functions in the cell. Lysosomes break down biological polymers to get rid of cell debris. On the other hand, vacuoles help store and transport material within and outside the cell. Besides their function, they also vary in their form and composition.
Let’s tell you all differences between lysosomes and vacuoles for better understanding.
Comparison Table
| Factors | Lysosomes | Vacuoles |
| Discovery | 1955 | 1676 |
| Presence | Eukaryotic cells | Almost all cells |
| Quantity | Hundreds | One in plants, a few in other cells |
| Types | Primary, secondary, autophagic, & residual bodies | Food, gas, sap, and contractile vacuoles |
| Origin | Trans-Golgi apparatus | Fusion of membrane vesicles |
| Functions | Breakdown of macromolecules | Storage of material |
| Components | Hydrolytic enzymes | Fats, water, waste material |
| Bursting | Autolysis | Cell harm |
What are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are cell vesicles containing enzymes and chemicals to digest macromolecules. They were first discovered by Christian de Duve in 1955, who also coined the term for them. Lysosomes are also widely known as ‘suicide bags’.
Lysosomes are small sacs of fluid with a single membrane. They are only found in animals, but absent in fungi, plants and prokaryotes. Humans have 300 lysosomes on average that transport molecules within the cell and break down waste products.
Structure of Lysosomes
Lysosomes are quite small in size, between 0.1 to 0.5 microns. Yet, you may also find some larger ones up to 1.2 micrometers. They are formed by the budding of the Golgi apparatus and obtain enzymes from the endoplasmic reticulum. The enzymes are transported to the Golgi bodies that pack them into lysosomes.
Their outer membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that encloses fluids with hydrolytic enzymes. The pH of the lysosomes is around 5, enabling the function of hydrolytic enzymes. Over 60 enzymes in lysosomes break down a wide variety of cellular molecules. The enzymes typically include lipases, nucleases, amylases, proteases, etc. Each of them breaks down specific molecules.
Lysosomes Functions
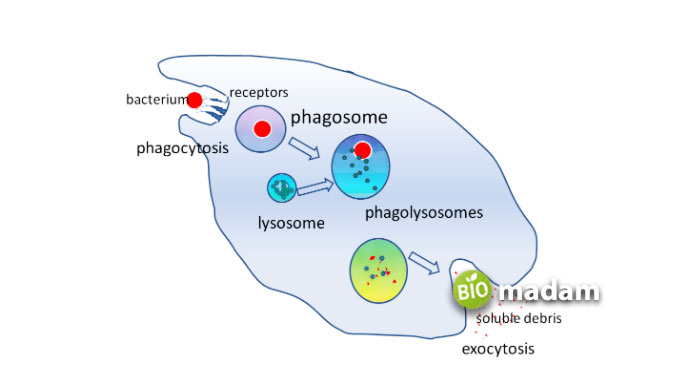
Lysosomes have essential functions in animal cells, just like any other organelle, i.e., ribosomes. The main function of lysosomes is to engulf and break down macromolecules, a few of which are macronutrients. These include lipids, carbohydrates and proteins, besides nucleic acids. The enzymes break down the larger molecules by adding water molecules to them. Some other functions of lysosomes regarding the digestion of wastes include:
- Digestion of organelles within the cell through autophagy
- Phagocytosis destroys antigens and pathogens like bacteria
- Breaking down food molecules by fusion with an endocytic vesicle
What are Vacuoles?
Vacuoles are vesicles found in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including algae and fungi. The vacuoles in animals are different from vacuoles in plants. Animals may have multiple small vacuoles, while plants have one large central vacuole. It may occupy up to 80% of the space in the plant cell.
Vacuoles are generally empty sacs that protect the components inside them. They are used to store or excrete damaged or engulfed materials in the cell. Eventually, they also save the cytosol from exposure to the damaged cell components. However, vacuoles have a semi-permeable membrane and allow the movement of only specific molecules.
Structure of Vacuole
Vacuoles are covered with a phospholipid semi-permeable membrane which may differ in organisms. The membrane covering vacuoles is known as tonoplast. The tonoplast contains proteins that help transport materials across the membrane and offer it a particular shape. Vacuoles are hollow and do not contain anything besides the molecules that must be transported or excreted out of the cell.
Vacuoles Functions
Vacuoles in animals and plants are involved in various functions besides storing and transporting materials. Vacuoles allow the toxic and deteriorated material to be kept away from the cytosol or cytoplasm due to the membrane. Let’s tell you how vacuoles perform and facilitate functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Vacuoles carry the substances secreted by secretory cells and labeled by the Golgi apparatus for distribution.
- Fat cells store large amounts of lipids in specialized vacuoles in single cells.
- The large vacuole in plants helps store water and maintains turgor pressure within the cell.
- Besides, the large vacuole help in the protection and growth of the plant cell.
Similarities Between Lysosomes and Vacuoles
- Eukaryotic cells have both cellular organelles.
- Lysosomes and vacuoles are sac-like vesicles that store and transport materials across cells.
- They are covered by a phospholipid membrane.
Differences Between Lysosomes and Vacuoles
Definition
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles in animals that contain hydrolytic enzymes to break down macromolecules.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that perform storage and transport functions in the cell.
Discovery
Lysosomes
Christian de Duve discovered lysosomes in 1955. He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974.
Vacuoles
On the other hand, Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovered the vacuole first in 1676.
Presence
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are only found in animal cells and are absent in plants, bacteria, and archaea.
Vacuoles
On the contrary, vacuoles are found in almost all organisms, including prokaryotes.
Quantity
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are present in large quantities in animal cells.
Vacuoles
Alternatively, plant cells have one large vacuole while animal cells have a few smaller ones.
Types
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are typically categorized into four types: primary, secondary, autophagic vacuoles, and residual bodies.
Vacuoles
Conversely, vacuoles are divided on the basis of their function into food vacuoles, gas vacuoles, sap vacuoles, and contractile vacuoles.
Origin
Lysosomes
Lysosomes form through budding off from the trans-Golgi membrane.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are produced by the fusion of membrane vesicles, forming a larger sac.
Function
Lysosomes
Lysosomes majorly contribute to the breakdown of damaged material and macromolecules.
Vacuoles
At the same time, vacuoles play a significant role in the storage of material.
Components
Lysosomes
Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes that help in the breakdown of substances.
Vacuoles
On the contrary, vacuoles store water, fats, waste material, etc.
Bursting
Lysosomes
Lysosomes bursting in the cell lead to autolysis of the cell.
Vacuoles
However, the bursting of the vacuole will disperse the components into the cytosol and harm the cell.
The Bottom Line
Lysosomes and vacuoles are sac-like membrane-bound organelles present in cells. Vacuoles are present in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in varying quantities. However, Lysosomes are only found in animal cells. The main difference between lysosomes and vacuoles is their composition. Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes to break down large molecules. Alternatively, vacuoles contribute to cell shape and storage of material. Both are essential to living cells to store and transport cells within and outside of the cell.
FAQs
Is lysosome bigger than vacuole?
Lysosomes are smaller and present in a large quantities in cells, with up to 1000 lysosomes per cell. On the other hand, vacuoles are comparatively bigger and found in less quantity. Plant cells contain only one large vacuole that takes up 80% volume of the cell.
What are the 3 types of vacuoles?
Cells typically have four types of vacuoles, including food vacuoles, contractile vacuoles, sap vacuoles, and gas or air vacuoles. They store and process different materials present in the cell.
How many vacuoles are in an animal cell?
There is no particular number of vacuoles in animal cells. They may vary from two or three to multiple in one cell. Contrarily, plant cells have one large vacuole that stores water and maintains turgor pressure.
What is the main difference between a vacuole and a vesicle?
Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that facilitate storage and transport in cells. Vesicles may fuse with other membranes in the cell, whereas vacuoles do not fuse with any membrane in the cell. They are also larger than vesicles.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.