While animals and plants are all important organisms in the food chain and food web, plants have a unique ability; they produce their own food using sunlight. So, plants produce all the necessary nutrients, such as proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. Carbohydrates are a fundamental energy source for all living organisms, but what is the function of carbohydrates in plants?
Carbohydrates perform two basic functions in plants: growth and metabolism.
This article brings you all the information regarding the role of carbohydrates in plants and their importance. Let’s tell you everything about it!
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients besides fats and proteins. The common structure of carbohydrates comprises carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen molecules, with the general formula C6H12O6.
Carbs are categorized into three groups, including sugars, starches, and fiber. Sugars are simple carbohydrates found naturally in vegetables, fruits, and milk. On the other hand, starches are complex carbohydrates found in cereals, bread, and pasta; your body breaks down starches into sugars first. Fibers are also complex carbohydrates, but your body does not metabolize them. Instead, they facilitate healthy gut health.
How do Plants Produce Carbohydrates?
Before we dive into the functions of carbohydrates in plants, here’s an overview of how plants manufacture carbohydrates.
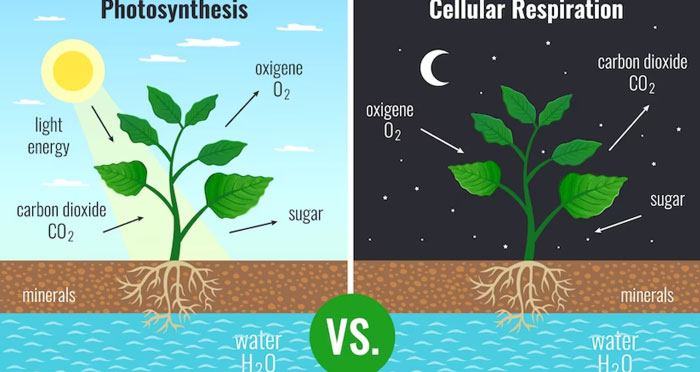
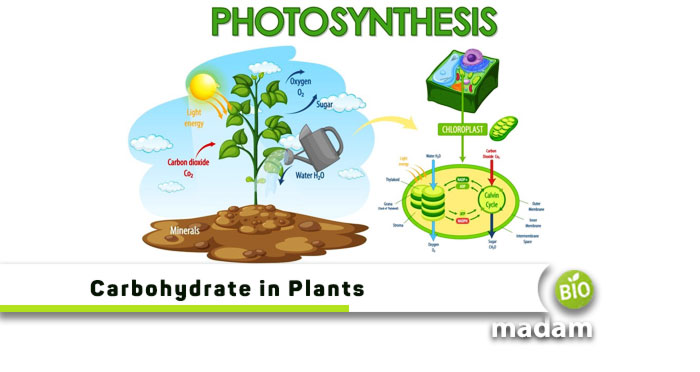
Plants use photosynthesis to produce carbs using sunlight and carbon dioxide to convert them into sugar molecules. Sunlight acts as the energy source to build bonds and form carbohydrate molecules. Plants use these molecules to carry out different processes. The following equation represents photosynthesis:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Functions of Carbohydrates in Plants
Cellular Respiration
Plants use glucose molecules produced by photosynthesis to generate energy through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration comprises three steps that break down glucose to yield individual molecules and electrons; the process yields 36 ATP molecules that power chemical reactions.
The first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis or the breakdown of carbohydrate molecules. Large polysaccharides are complex molecules with multiple chemical bonds, making them an excellent energy reserve. Metabolism of these molecules during cellular respiration results in energy liberation.
Plants store excess carbohydrates in the form of starch, ready to disintegrate and produce energy when needed. These starch molecules come into use when the plant needs more energy.
The process of using glucose molecules to produce energy through cellular respiration is as follows:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Biochemical Synthesis
Besides energy production, carbohydrates also contribute to biochemical synthesis in an organism’s body. Carbohydrate breakdown leads to carbon atom release that acts as raw material to produce other molecules. As polysaccharides are complex molecules, their metabolism takes time, providing enough time for bodily functions and biochemical synthesis in plants.
Cell Wall Production
Cell walls are important plant cell structures, and polysaccharides, including hemicellulose and cellulose, are an important element of the cell wall. Carbohydrate breaks down and releases chemicals that help strengthen the structure by providing a specific framework. Plant cells might not be able to grow or stand in case cell walls were absent.
Signaling Molecules in Immunity
Carbohydrates in plants are excellent signaling molecules in immunity, leading to “sugar-enhanced defense” and “sweet-immunity” concepts by researchers. They are usually associated with small sugar molecules such as mono or disaccharides or small oligosaccharides that activate plant defense responses. These responses eventually increase plant resistance to antigens and pathogens, e.g., sucrose induces isoflavonoid synthesis in defense against Fusarium oxysporum.
Metabolism and Abiotic Stress
Another important role of carbohydrates as signaling molecules is their impact on abiotic and biotic stress. While research reveals that carbohydrates do not directly influence abiotic stress responses, evidence shows they are necessary for a communication system that responds to environmental stresses. Carbohydrates such as sucrose and fructans are also critical to ROS produced by plants in response to abiotic stresses. Furthermore, sugars contribute to antioxidant activity as they have ROS-scavenging properties.
The Bottom Line
Carbohydrates are one of the three macromolecules that enable proper functioning in plants and animals. However, carbohydrates in plants have some specific functions absent in animals. Besides acting as energy sources, the functions of carbohydrates in plants include yielding energy through cellular respiration, contributing to immunity as signaling molecules, and facilitating cell wall production. They also have a role in protecting the plant against biotic and abiotic stress.
FAQs
What are the 3 uses of carbohydrates in plants?
Plants use carbohydrates to produce energy through cellular respiration and help protect the plant against environmental stress. Furthermore, carbs are converted into cellulose and hemicellulose to build cell walls.
What are carbohydrates in plants called?
Carbohydrates in plants are also called carbohydrates, but they are stored in the form of starch in plants, while animals store them as glycogen. They act as energy sources when needed and contribute to various cellular and bodily functions.
Do plants need carbohydrates to grow?
Yes, carbohydrates are essential to plant growth and metabolism to produce energy for various processes. Animals obtain carbohydrates from other food sources, but plants manufacture carbohydrates through photosynthesis. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water in sunlight for energy production.
What is the major function of carbohydrates in plants and animals?
Carbohydrates have specific functions in plants and animals, but energy storage is the most common in both. Carbohydrates, especially starches, are complex molecules that liberate a high amount of energy on breakdown. Similarly, carbohydrate molecules contribute to ATP production through cellular respiration.
Are carbohydrates in all plants?
As carbohydrates are essential to plant growth and survival, all plants have carbohydrates. They provide the energy to produce cell walls which are an integral part of the plant cell. They are also vital to immune signaling.
Why is it important that plants store carbohydrates as starch?
Plants store carbohydrates in the form of starch instead of any other molecule or compound, as they are easy to break down to obtain energy. Starch metabolism liberates energy faster than fats or proteins. Thus, plants store carbohydrates as starch.

Hi, my name is Eva. I am currently practicing as a clinical social worker, that being my childhood desire. As a licensed therapist holding MPhil in Clinical Psychology, I am now on biomadam to provide the natives with the best family advice! Do you have any questions? See you in the comment section.