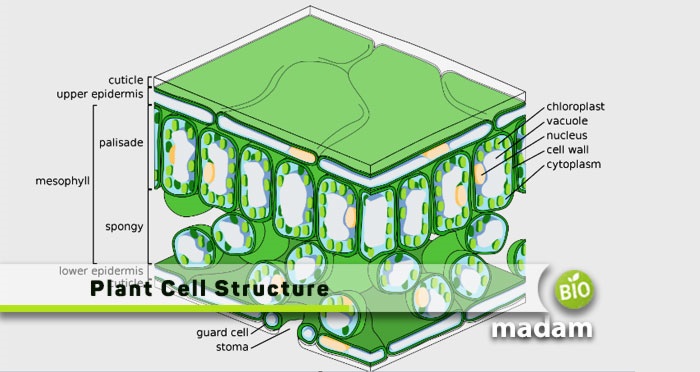
Plants are eukaryotic organisms comprising of numerous cells. There are different eukaryotic cells that vary in different organisms, e.g., unicellular eukaryotes and multicellular eukaryotes. Plants are basically the multicellular eukaryotes having mitochondria and chloroplasts. Another important component is the cell wall that is specific to fungi, algae, and plants only.
So, what’s the need for the cell wall? Keep reading to learn about the function of the cell wall in the plant cell.
Plant Cell Wall Structure
In a plant cell, a cell wall is the outermost, non-living component present outside the cell membrane. It is permeable and allows the passage of certain molecules. The cell wall acts as a barrier between the cell and the external environment. It also provides a rigid shape to the plant cell that animal cells comparatively lack.
Plant cell wall comprises long, strong fibers of cellulose. It is the most abundant macromolecule on Earth, composed of hundreds of glucose molecules. The long fibers join together to form bundles called microfibrils which produce polysaccharides. Cellulose is present in wood and fiber. While plants and fungi both have cell walls, the composition varies. Fungal cell walls are made of chitin compared to cellulose in the plant cell wall.
Components of Plant Cell Wall
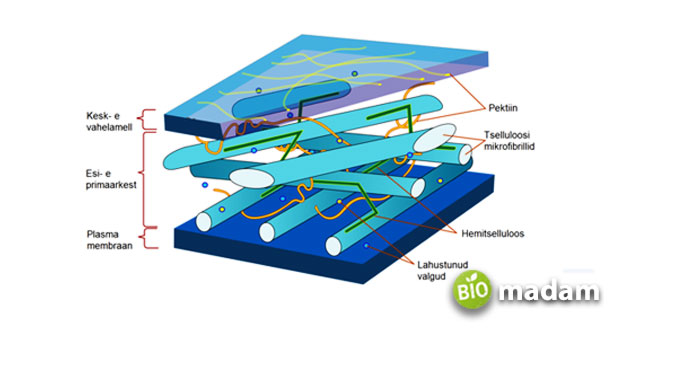
The plant cell wall looks like a simple outer covering but comprises three layers: primary cell wall, middle lamella, and secondary cell wall.
Primary Cell Wall
The primary cell wall is next to the cell membrane and forms before the secondary cell wall. It is composed of cellulose and stretches as the plant grows. It also allows molecules to pass through it because of increased permeability. Cells of the primary wall in plants contain proteins and polysaccharides.
Secondary Cell Wall
The secondary cell wall is between the primary cell wall and the cell membrane. It forms inside the primary cell wall once it matures. The secondary cell wall acts as the main part of the cell wall responsible for strengthening and supporting the cell. It contains lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose. Lignin facilitates water conductivity, besides providing rigidity to the cell structure.
Middle Lamella
The middle lamella is present on the outside and contains pectin. Pectin allows the layer to connect to the cell wall of the neighboring cells acting as glue. It also contains other components like proteins and lignin.
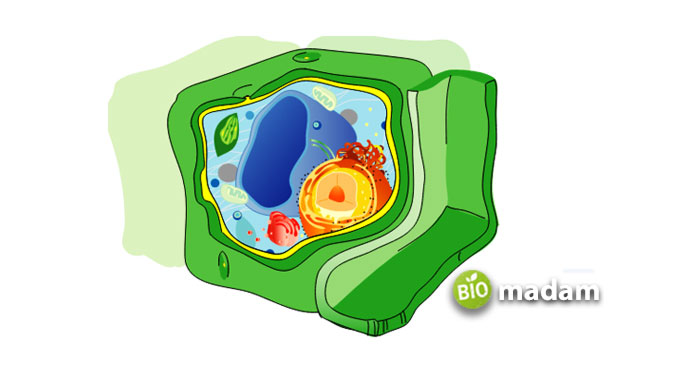
Functions of Cell Wall in Plant Cell
The main function of the cell wall is to strengthen the plant cell membrane and provide a proper shape to the plant cell. However, it also plays a few other functions, including:
Support
The cell wall in plants provides support and mechanical strength to the cell besides giving it a definite shape. It also controls and regulates the direction of the cell’s growth in vascular and nonvascular plants. The cell wall provides rigidity to the plant cell to maintain its shape.
Protection Against Stress
The cell wall plays a major role in protecting the plant against physical shocks and mechanical stress. The rigidity of the cell wall also allows it to withstand the turgor pressure. The cell organelles exert turgor pressure on the cell wall as they push the membrane against it. While this pressure is critical to the cell’s shape, it may burst if the cell wall is not present.
Maintains an Internal Environment
The cell wall acts as a barrier between the external environment and the inner components of the cell. The permeability allows communication with the external environment without disturbing the internal setting.
Communication with Other Cells
The plasmodesmata or pores between plant cell walls allow the transfer of signals among the cells.
Preventing Water Loss
The cell wall provides a thick covering to the cell and protects it from dehydration due to water loss. An adequate amount of substances within the cell is critical to cell growth and sustenance. Thus, the cell wall ensures that enough water stays within the cell.
Storage
The cell wall is a site for storing carbohydrates required for the plant’s growth. It especially plays a significant role in developing seeds.
Transport of Material
The cell wall enables the transport of material in and out of the cell per need. Important molecules move inside the cell while waste materials are expelled outside the cell through the cell membrane.
Protection
Besides providing support and storing carbs, the plant cell wall also plays a major role in protecting the plant against parasites, bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
The Bottom Line
The cell wall is an additional organelle in fungi, algae, and plants. It provides a definite structure to the plant cell and boosts strength. It also has a major role in protecting the plant against antigens and pathogens. The plant cell wall comprises three layers: primary cell wall, secondary cell wall, and middle lamella. They together form a rigid layer outside the cell membrane to protect the internal environment and support the cell.
FAQs
What are the characteristics of the plant cell wall?
Plants are eukaryotic organisms having a rigid cell wall structure. It comprises cellulose and is composed of microfibrils that produce polysaccharides that form the cell wall.
What are plant cell walls called?
The plant cell walls are composed of the primary cell wall, the secondary cell wall, and the middle lamella. They facilitate communication between the cells and allow the transport of movement.
What is the shape of the cell wall?
The plant cell wall is in the shape of a cylinder, and its structure helps protect the cell against external stress.
Is cell wall living or dead?
The outermost layer of the cell, the cell wall, is a dead component of the cell. It distinguishes the cell’s internal environment from the external.
What color is plant cell?
Plant cells appear green due to the presence of chloroplasts, absent in animal cells. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll a and b, giving the characteristic green color.
Can a cell live without a cell wall?
Most bacteria have cell walls, but others can survive without them. Their cytoplasmic membranes are tough and protect them from environmental changes, eliminating the need for a cell wall.

The Biomadam Content Team develops and manages educational and informational articles published on Biomadam. Content is prepared using standard reference materials and follows internal editorial guidelines to ensure clarity and consistency.