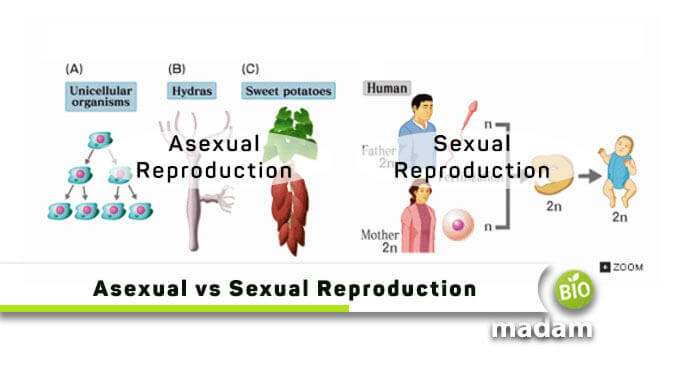
Before checking the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction, everyone would have an idea that there is only one organism involved in asexual reproduction. In contrast, sexual reproduction acquires the participation of both males and females. Many organisms reproduce either sexually or asexually, whereas a few necessitate both. For instance, most unicellular organisms and some plants can reproduce asexually, whereas fish and mammals have sexual mechanisms. However, many other creatures like komodo dragons and corals can replicate both.
Despite everything, the organisms produced asexually wouldn’t have the genetic variation, so they’ll have a lesser ability to adapt to the surrounding environment. Let’s check out the comparison chart briefly!
Comparison Table
| Parameters | Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
| Parental Type | Bi-parental | Uniparental |
| Gamete Formation | Yes | No |
| Cells Involved | Germs Cells | Somatic Cells |
| Type of Cell Division | Mitosis & Meiosis | Only Mitosis |
| Progeny | Genetically Different | Genetically Identical |
| Parent Cell Traits | Presents Both Parents’ Traits | Only One Parent Traits Inherited |
| Types | External Fertilization, Conjugation, Syngamy | Fragmentation, Budding of Hydra, Spore Formation |
| Nature of Process | Slow | Rapid |
| Examples | Humans, Plants, Animals, etc. | Bacteria & Some Protists |
What is Sexual Reproduction?
This type of reproduction occurs when two sex cells/gametes from opposite individuals combine to produce a zygote, unique offspring. This mechanism is highly complex compared to asexual reproduction, where the produced offspring has numerous new genes. The process involves both mitosis and meiosis steps. Meiosis, further classified in type I and II, results in half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell through recombination and crossing over.
You must have observed genetic variations in organisms undergoing sexual reproduction. That is because of the initial meiosis I stage, where the crossing over of chromosomes produces a new haploid daughter chromosome. Besides that, every other step in the entire reproduction process holds great significance. For instance, the gestation period during the cycle is important for a fetus to fully grow – be it inside a mother’s womb or in an egg. Sexual reproduction has a vital role in bringing variations in the ecosystem through the fusion of gametes and cell division. These variations are indirectly linked to the survival of several species in an environment.
What is Asexual Reproduction?
As the name suggests, this type of reproduction doesn’t involve any sex gametes and functions through mitosis, including cytokinesis and karyokinesis. One cell divides to form identical daughter cells. Moreover, the cells formed have exactly the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cells, unlike sexual reproduction. Asexual reproduction lacks meiosis and its different steps; thus, few genetic variations are seen. However, sudden mutation can result in minor variations in the resulting generation. Overall, the entire process is simple and time-saving.
There are a couple of other advantages of asexual reproduction. Besides saving energy, the process is pretty rapid and grows quickly into a whole population. On the contrary, the process also has some cons, where the primary is limitations in genetic variations. In other words, if a natural disaster attacks an environment, there are chances of the entire asexual generation to eradicate. Common examples include bacteria and some protists.
Differences between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Now we will walk you through the major differences between both reproduction types. So let’s get started.
Further Types in Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
The two main types of sexual reproduction are Syngamy and Conjugation.
Syngamy: is the permanent union of two haploid gamete cells to produce a zygote. It is known as fertilization in human beings.
Conjugation: is another type of sexual reproduction that is temporary and utilizes a cytoplasmic bridge. This type is commonly observed in bacteria, passing DNA of the prokaryote across the bridge.
Asexual Reproduction

We have come across several types of asexual reproduction until now. These consist of gemmules and budding, where the organisms reproduce by releasing a special mass from parent cells, or the organisms grow out of the parent’s body, respectively. Below are a few types of asexual reproduction:
Fragmentation: is held when a parent cell breaches into fragments that grow into a new individual. Starfish is a common example. It can reproduce from just a single arm or ray. However, starfish also show sexual reproduction.
Binary Fission: Contrary to fragmentation, binary fission involves splitting a parent cell into two similar daughter cells.
Budding: Similarly, contrary to fragmentation and binary fission, budding occurs when a bubble-like bud is formed from a parent cell. Throughout its growth and development, it remains attached to its parent cell. After the complete procedure, it detaches itself from the parent cell. A common example is “budding in yeast.”
Process

Sexual Reproduction
This type of reproduction engages both males and females of similar genus and species to get their genetic material. Through meiosis, these genetic material forms gametes and gets half chromosomes individually, called haploid gametes. Fertilization processes when these two gametes unite and produce a diploid zygote having its own inheritable material.
Asexual Reproduction
This type of reproduction is held without combining two members of the same species. The division of cells is done through mitosis, where every chromosome cell makes a copy before nucleus division. This way, each new cell gets a piece of identical genetic information.
Example
Sexual Reproduction
There are numerous examples of sexual reproduction, including fishes, most mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects.
Asexual Reproduction
Different organisms like bacteria, spider plants, yeast, and jellyfish follow asexual reproduction. Multiple identical twins are created by this method.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Sexual Reproduction
The biggest advantage of sexual reproduction is that it promotes variation, helping evolve. It then creates species that adapt themselves to new surroundings. It is beneficial in preventing different diseases and infections from attacking. However, it has a central drawback of using a significant amount of energy to mate with its partner.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction is perfect for organisms sticking to one place and those who cannot move with the change in environment. Asexual reproduction is usually adopted by simple creatures, like bacteria. However, it has the disadvantage of not producing variations in its daughter cells. All individuals are identical to each other, which are very easy to wipe out by a specific disease or change in surroundings.
Conclusions
After a thorough discussion on the difference between sexual and asexual reproduction, we understood that both are forms of promoting one’s generation, in either way. If the former type involves two parents to produce offspring, the latter can replicate by the engagement of only one parent. Last but not least, both types of reproduction retain their own importance.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.