Recently updated on March 7th, 2023 at 02:14 am
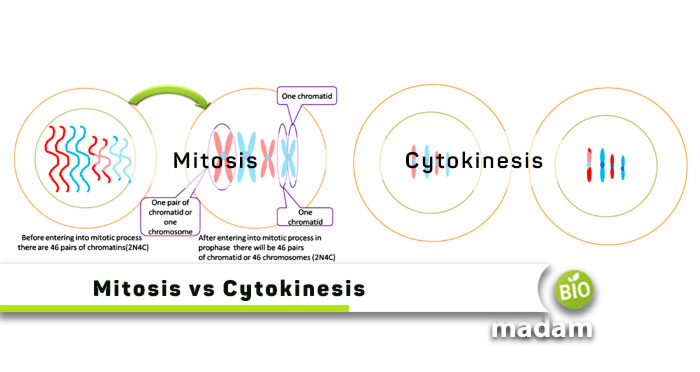
Mitosis and cytokinesis are cell division processes contributing to sexual and asexual reproduction. Both processes come up with cell division and reproduction in their unique ways. Mitosis leads to the formation of two nuclei from the parent cells, while cytokinesis refers to the division of the cytoplasm. Both these processes eventually lead to the production of new cells.
Let’s tell you the differences between mitosis and cytokinesis in detail.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Mitosis | Cytokinesis |
| Definition | Nucleus division | Cytoplasm division |
| Phases | Yes | No sub-phases |
| Division | After interphase | After mitosis |
| Product | 2 daughter nuclei | 2 daughter cells |
| Karyokinesis | Present | Follows karyokinesis |
| Sequence | First | Later |
| Time Consumption | Less | More |
| Nature | Same in all cells | Different for plants & animals |
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of duplication and distribution of chromosomes containing genetic information. During mitosis, cell duplication, or reproduction, a single cell produces two genetically identical daughter cells. Mitosis helps eukaryotes in development and growth. It also plays a role in asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms. Mitosis splits a cell’s replicated DNA into two new nuclei.
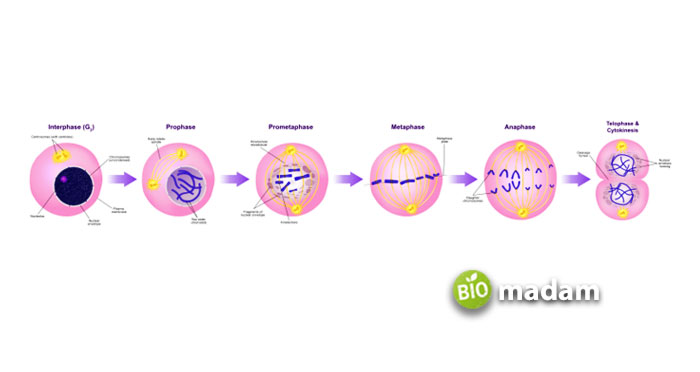
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis comprises five general steps that take place in different types of eukaryotic cells.
Interphase
Nucleus has a primary role in the stages of mitosis as the cell growth phase or interphase occurs just in the nucleus before mitosis. It is further broken down into the G1 phase and S phase.
G1 Phase: This is the stage preceding DNA synthesis.
S Phase: DNA synthesis happens during this phase.
G2 Phase: Between the end of DNA synthesis and the start of prophase, the G2 phase occurs.
Prophase
The duplicated genetic material shrinks and pack together during prophase. After S and G2, mitotic cells condense the chromatin material into compact chromosomes during prophase.
When chromosomes, having the genetic material DNA, replicate, they form sister chromatids linked at the centromere of the chromosome. At each cell pole, long proteins known as microtubules assemble into a substantial structure known as the mitotic spindle.
Prometaphase
The disintegration of the nuclear envelope initiates during prometaphase. As a result, microtubules can now reach from the centromere to the chromosome. Kinetochore attachment to microtubules permits chromosomal movement throughout the cell.
Metaphase
The step after the prometaphase is the metaphase. During metaphase, the microtubules tug on the sister chromatids until they align on the equatorial plane, which runs down the middle of the cell. The metaphase plate is the term for this area. In this way, the entire genome is fully functional in each cell.
Anaphase
Sister chromatids undergo a synchronous separation at their respective centromeres during anaphase. Once the chromosomes untangle, the spindle will draw them to opposing ends of the cell. The process of anaphase guarantees that each daughter cell will have the same number and set of chromosomes.
Telophase
Mitosis constitutes telophase as the last step of the process. A nuclear membrane surrounds each set of chromosomes during telophase, isolating the DNA from the cytoplasm. The chromosomes lose their coil and become more dispersed.
Significance of Mitosis
- Mitosis is responsible for developing plants’ new shoots, roots, stems, and leaves.
- No recombination or crossing over occurs during mitosis, which aids in keeping the genome intact.
- In animals, it is responsible for regenerating worn-out or injured tissues and organs, including the epithelium tissues in the intestine, blood cells, and other tissues and organs.
What is Cytokinesis?
Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes complete their cell division through a process called cytokinesis. Cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm into two, leading to the formation of two distinct cells. It is the process by which chromosomes separate during cell division, and it begins during anaphase and concludes during telophase in the vast majority of cells.
Cytokinesis is the physical division of the cytoplasm, cell membrane or plasma membrane, and organelles in eukaryotic cells. It generates two separate compartments after the cell cycle in mitosis and meiosis.
Stages of Cytokinesis
There are four distinct stages of cytokinesis in animals and many unicellular eukaryotes.
Initiation/Cleavage Furrow Development
As cytokinesis begins, the first visible alteration is the formation of the cleavage furrow. Eventually, the furrow will become so deep that it will split the cell. The contractile ring is the structure responsible for cleavage. Actin filaments, myosin II filaments, and proteins like regulatory proteins make up the contractile ring. The position of the contractile ring, and hence the plane of cell division, is set by the mitotic spindle fibers.
Contraction
The contractile ring components accumulate just beneath the plasma membrane and contract to constrict the cell into two. It is also sometimes called abscission.
Insertion of Membrane
As the cell contracts, intracellular vesicles fuse to generate a new membrane next to the contractile ring. The new membrane allows the cell to grow as the cytoplasmic division occurs.
Completion
The process of cell division is completed by tightening the contractile ring and creating a new membrane to bridge the gap left by the mother cell’s division into two daughter cells.
Significance of Cytokinesis
- The development of the block-cytokinesis micronuclei cytome assay for studying human lymphocytes results from research into this cellular process.
- Incomplete cytokinesis processes might contribute to carcinogenesis. Understanding cytokinesis has helped advance our knowledge of oncogenesis and pharmacological targets for cancer treatment.
Similarities Between Mitosis and Cytokinesis
- Cytokinesis and mitosis are two mitotic cell division processes.
- Both steps are crucial for the production of new daughter cells.
- Mitosis and cytokinesis ensure that the number and type of chromosomes is equal in new cells.
Difference Between Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Definition
Mitosis
A single nucleus undergoes mitosis to divide into two identical daughter nuclei.
Cytokinesis
On the other hand, cytokinesis splits a cell’s cytoplasm into two daughter cells after proceeding through karyokinesis.
Karyokinesis
Mitosis
Mitosis solely includes karyokinesis and cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis
However, cytokinesis involves the division of the cytoplasm after karyokinesis.
Sequence
Mitosis
Mitosis precedes cytokinesis.
Cytokinesis
While cytokinesis happens after mitosis.
End Product
Mitosis
Mitosis gives rise to two nuclei.
Cytokinesis
On the other hand, cytokinesis generates two distinct cells.
Time Consumption
Mitosis
This process consumes comparatively small amounts of time.
Cytokinesis
Alternatively, cytokinesis needs more time to complete.
Occurrence
Mitosis
The mitotic process is the same for all eukaryotic cells.
Cytokinesis
Conversely, plants and animal cells have specific cytokinesis processes.
The Bottom Line
Mitosis and cytokinesis are cell division processes in eukaryotic cells that contribute to growth and development. On the other hand, they enable asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms. Mitosis primarily replenishes and allows growth and development to ensure a healthy body. The main difference between mitosis and cytokinesis is that mitosis divides the nucleus while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm. Cytokinesis occurs after mitosis. This leads to the formation of two distinct daughter cells.
FAQs
What is the difference between cytokinesis in mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis occurs in all living cells, while meiosis takes place only in reproductive cells to differentiate X and Y chromosomes. The reproductive cells undergo division twice, and cytokinesis is a part of both processes. On the other hand, mitosis comprises cytokinesis only once.
What is the relationship between cytokinesis and mitosis?
Mitosis and cytokinesis are the two parts of cell division, ensuring uniformity. Mitosis divides the cell nucleus into two, while cytokinesis ensures both cells receive one nucleus.
What is the major difference during cytokinesis?
The process of cytokinesis varies in plants and animals due to the absence of cell walls in animals. Plants experience cytokinesis through the cell plate method, while animal cells follow the cleavage furrow method.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.