Recently updated on October 30th, 2023 at 09:59 am
Fragmentation, binary fission, and budding are common asexual reproduction methods. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes use these methods to multiply without gametes. Binary fission gives rise to two cells from one parent cell, while fragmentation leads to the breakage of the parent cell into many. Binary fission is common in archaebacteria, eubacteria, and protists. Alternatively, fragmentation takes place in many multicellular organisms like plants. Keep reading to learn more about binary fission and fragmentation.
Comparison Table
| Factors | Binary Fission | Fragmentation |
| Definition | Division into two cells | Breakdown into multiple fragments |
| Type of Cell | Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes | Multicellular |
| No. of Cells | Two | Multiple |
| Karyokinesis | Present | Absent |
| Examples | Bacteria and archaea | Sea stars, molds, algae, and plants |
What is Binary Fission?
Binary fission is the breakdown of a parent cell to give rise to two daughter cells. The process takes place through cytokinesis and mitosis to produce new organisms. The cytoplasm and the nucleus divide equally between the two cells. It is one of the most prominent differences between binary fission and other asexual reproductive methods. It is also a common factor between sexual and asexual reproduction, that it typically divides the cell components equally among both daughter cells. Binary fission is also known as prokaryotic fission, as it is more widely adopted by prokaryotes. Bacteria and archaea exhibit this type of asexual reproduction. Besides binary fission, multiple fission is an asexual reproduction method that produces multiple cells.
Binary Fission Process
- Binary fission begins with the uncoiling of DNA and chromosomes in the cell.
- Specific chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell for karyokinesis.
- Cytokinesis occurs following karyokinesis to distribute cell components equally.
- A cleavage furrow forms that separates the plasma membrane, forming two cells from one.

Example
Amoeba is the most widely known example of binary fission. This organism divides through this process into two, which continues in all generations to reproduce. The two smaller cells grow into the size of the original cells. Body organelles like mitochondria also multiply through binary fission.
What is Fragmentation?
Fragmentation is another method of asexual reproduction commonly occurring in multicellular organisms. Fragmentation refers to the breakdown of a parent cell or organism into smaller parts or fragments that grow into individuals. Fragmentation takes place in prokaryotic and some types of eukaryotic cells. The ability of colonial organisms to divide through fragmentation gives rise to the name “colonial fragmentation.”
Besides yeast and bacteria, fragmentation is widely adapted by lichen, molds, cyanobacteria, plants, fungi and animals. It is common in starfish, sea stars, and acoel flatworms as well. Colonial animals like corals and sponges also use fragmentation to multiply. Vegetative propagation in plants takes place through this process. Fragmentation helps in the production of bulbs, rhizomes, and stolons. Sometimes fragmentation may also occur undeliberately. Fragmentation involves mitosis instead of meiosis.
Fragmentation Process
- Fragmentation takes place through the formation of furrows along the points of splitting.
- The cell eventually breaks from that particular point.
- The broken fragments regenerate the missing pieces as the tissues and organs grow again.
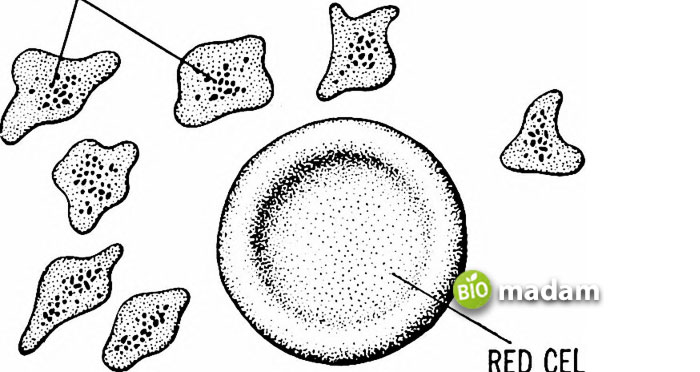
Animals utilize dichotomy and paratomy to form fragments that grow into new organisms. Dichotomy takes place at a particular point where the tissues and organs regenerate. At the same time, paratomy is the breakdown of the organism perpendicular to the antero-posterior axis.
Example
The development of sea stars takes place through fragmentation. The large fragment from the parent gives rise to a new individual that might be smaller in size than the parent. The fragment eventually develops into a proper organism through regeneration.
Similarities between Binary Fission and Fragmentation
- Binary fission and fragmentation are modes of asexual reproduction.
- They both are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- These processes produce identical cells or organisms.
Differences between Binary Fission and Fragmentation
Definition
Binary Fission
Binary fission is the breakdown of parent cells to produce two similar daughter cells.
Fragmentation
Contrarily, fragmentation gives rise to multiple fragments of an organism, growing into a new organism.
Number of Daughter Cells
Binary Fission
Binary fission results in the production of two daughter cells.
Fragmentation
At the same time, fragmentation may produce multiple fragments that grow into individuals.
Type of Cells
Binary Fission
Binary fission typically takes place in prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes.
Fragmentation
Meanwhile, fragmentation occurs in multicellular organisms majorly.
Karyokinesis
Binary Fission
Karyokinesis and cytokinesis take place during binary fission.
Fragmentation
While, fragmentation does not involve the division of the nucleus between daughter organisms.
Examples
Binary Fission
Binary fission is common in bacteria and archaea.
Fragmentation
Fragmentation takes place in cyanobacteria, sea stars, molds, fungi, algae, and plants.
The Bottom Line
Many organisms grow through asexual reproduction methods that do not involve oogenesis or spermatogenesis. Binary fission and fragmentation are two asexual reproduction methods utilized by prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The primary difference between the two is that binary fission produces two cells while fragmentation gives rise to multiple. Prokaryotes, like bacteria, typically reproduce through binary fission, while vegetative propagation in plants takes place through fragmentation. Some organelles also multiply with the help of binary fission.
FAQs
Is fragmentation a type of binary fission?
Binary fission may be considered a type of fragmentation as both result in pieces of the original cell. Binary fission results in two identical cells, while sometimes fragmentation may give rise to multiple identical cells.
What is the difference between fission regeneration and fragmentation?
Binary fission refers to dividing cells into two, whereas fragmentation gives multiple daughter cells. They all grow into independent organisms asexually. Regeneration allows an organism to grow a part of its body, such as a starfish that can generate its arms.
What is the difference between binary fission and cloning?
Cloning refers to creating identical organisms, and binary fission is a type of cloning called cellular cloning. The cell divides into two identical cells that grow on their own. Alternatively, mitosis in eukaryotes also follows cloning or binary fission for growth and development.
What is the difference between binary fission and multiple fission?
Binary fission and multiple fission follow the same basic mechanism of cell splitting for asexual reproduction. Binary fission results in two cells, whereas multiple fission may produce three cells or more.
What are some examples of fragmentation and regeneration?
Bacteria, fungi, plants, and smaller animals like starfish and sponges exhibit fragmentation. At the same time, starfish also go through regeneration, besides octopus.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.