Recently updated on October 4th, 2023 at 09:46 am
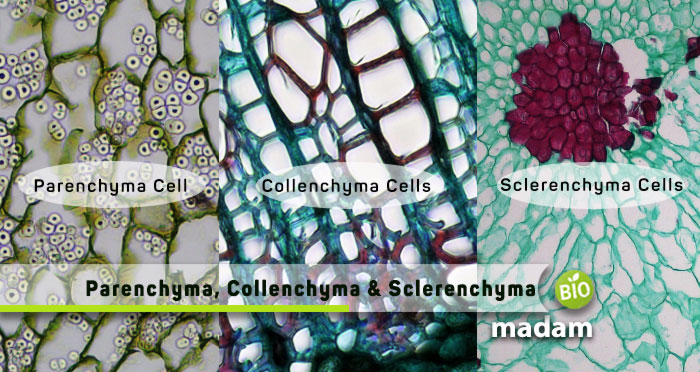
All kinds of plants comprise different cells and tissues contributing to functions like photosynthesis, cellular respiration, fermentation, etc. Despite the level of complexity of plants, all of them comprise parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells. Parenchyma cells have thin cellulose walls, whereas collenchyma cells have cell walls with thickened areas of additional cellulose. Alternatively, sclerenchyma cells have lignified cell walls.
Keep reading to learn all the differences between parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells.
Comparison Table
| Factors | Parenchyma Cells | Collenchyma Cells | Sclerenchyma Cells |
| Cell Type | Isodiametric cells | Elongated polygonal | Long, narrow cells |
| Occurrence | Fruits and leaves | Petioles and young stems | Matured stems |
| Function | Photosynthesis & gaseous exchange | Mechanical support and flexibility | Food transport and mechanical |
| Nature of Cell | Living | Living | Dead |
| Composition of Cell Wall | Cellulose | Cellulose, pectin, and hemicelluloses | Lignin |
| Thickness of Cell Wall | Thin | Unequally thin | Thick |
| Intercellular Spaces | Present | Absent | Absent |
What are Parenchyma Cells?
Parenchyma cells are simple living cells. They have a thin, elastic cell wall comprising cellulose and hemicellulose. These cells contain small vacuoles. Roots, stems, and leaves of all vascular plants contain parenchyma tissues. However, unlike vascular plants, non-vascular plants lacks these structures. Parenchyma cells in a leaf’s palisade tissues are elongated in shape. Some are in lobed forms in the palisade and spongy leaf tissues. At the same time, plant stems have stellate cells of parenchyma with well-developed air space.

Types of Parenchyma Cells
Parenchyma cells are categorized into different types based on their components and function.
- Storage Parenchyma: They serve as a food and water storage unit. Plants benefit themselves from the stored protein as a source of nitrogen.
- Chlorenchyma: Chlorenchyma cells present in the leaf help in photosynthesis.
- Secretory Parenchyma: They have resins and release sticky substances and other secretions.
- Aerenchyma: These cells have larger intercellular spaces for the gaseous exchange. They are present in aquatic plants to help them in their buoyancy.
Functions of Parenchyma Cells
- They help in the primary and secondary growth of plants.
- Parenchyma cells engage in meristematic activities such as wound healing, regeneration, and grafting.
- Because of chloroplast and mitochondria, mesophyll performs photosynthesis by using ATPs.
- Since the chromoplast is present in parenchyma cells, they give color to fruits and petals.
- They facilitate water storage in plants.
What are Collenchyma Cells?
Collenchyma cells are present in peripheral positions in the stems and leaves of dicotyledons. They play a major role in providing support to the plant. Their cell walls thicken at maturity. However, they are unevenly thick. Cellulose, pectin, and hemicelluloses are the constituents of their cell wall. They contain certain chloroplasts, and intercellular spaces are absent in them. Collenchyma cells exist at the spikes of herbaceous stems, petioles, and in ribs of some types of leaves. They can also appear in floral parts, fruit, and aerial roots. Collenchyma has long cells. In cross-section, the cell seems polygonal or oval. They are the living cells of the plant.
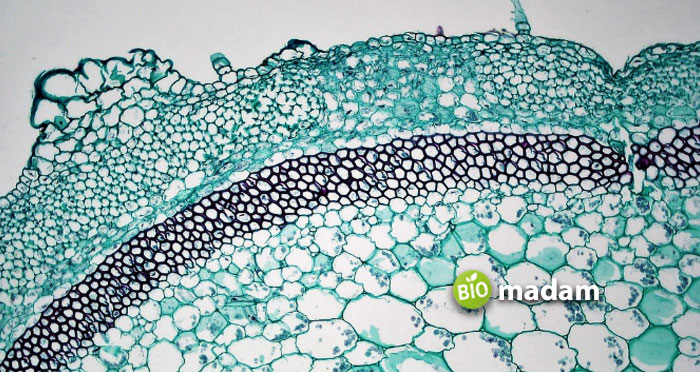
Types of Collenchyma Cells
Collenchyma cells are also categorized into four types of cells.
- Angular Collenchyma: The deposition of material that makes the thickening of the cell wall occur at the corner of the cell.
- Annular Collenchyma: They have a thick uniform and regular cell wall.
- Lacunar Collenchyma: These cells have air spaces between them
- Tangential Collenchyma: Cells arrange themselves in a row and make a thick layer at the tangential face of the cell wall.
Functions of Collenchyma Cells
- Collenchyma cells help in photosynthesis because of the presence of chloroplast.
- They provide mechanical support to the plant structure and plant growth.
- These cells also offer flexibility to young plants to allow easy bending.
What are Sclerenchyma Cells?
Sclerenchyma cells have a lignified cell wall with pits in them. These tissues are stiff because of a thick cell wall comprising lignin. Protoplasts are absent and therefore are dead cells of the plant. Mature sclerenchyma cells are usually rigid and non-stretchable. Consequently, they exist in non-growing parts such as the bark and stems. These cells are tubular and elongated in shape. They have narrow lumen due to thick cell walls.
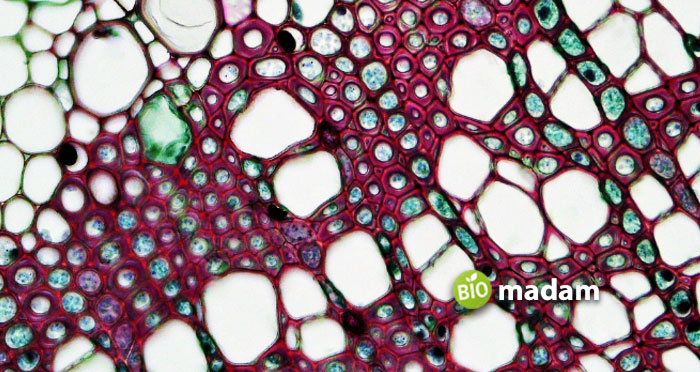
Types of Sclerenchyma Cells
The main types of sclerenchyma cells are fibers and sclereids.
- Fibers: They are long cells to a great extent and pointed ends. Fibers are present in vascular bundles of leaves, stems, and roots.
- Sclereids: These cells belong to the vascular tissues in plants (xylem and phloem). The sclereids in sclerenchyma possess a narrow lumen and thick cell wall that contains some pits with round aperture making the cell wall non-uniform.
Functions of Sclerenchyma Cells
- The primary function of the cell is to show mechanical support and strength.
- They create protective layers all over the nuts and seeds.
- They also constitute conductive tissues.
- Sclerenchyma cells make up the xylem vessels and tracheids.
- They make the hypodermis of xerophytic plants to prevent water loss.
Difference between Parenchyma, Collenchyma, and Sclerenchyma
Cell Shape
Parenchyma Cells
The parenchyma has isodiametric cells.
Collenchyma Cells
Collenchyma cells are elongated polygonal in shape.
Sclerenchyma Cells
Sclerenchyma cells have a long narrow cell structure with tapering ends.
Occurrence
Parenchyma Cells
Parenchyma, also known as “filler” tissues, is found in the soft parts of plants, such as fruits and leaves.
Collenchyma Cells
Collenchyma cells are present in petioles and a portion of the young stems.
Sclerenchyma Cells
They are dead cells that can only be found in matured parts like stem regions at the base.
Cell Wall Composition
Parenchyma Cells
The cell wall of the parenchyma is thin, and its composition is cellulose.
Collenchyma Cells
On the contrary, the cell wall of these cells is thick due to its constituents; cellulose, pectin, and hemicelluloses.
Sclerenchyma Cells
Besides, the cell wall of sclerenchyma cells is quite thick and rigid due to the presence of lignin.
Intercellular Spaces
Parenchyma Cells
The parenchyma has intercellular spaces between the cells.
Collenchyma Cells
In Collenchyma cells, intercellular spaces are absent.
Sclerenchyma Cells
But, on the other hand, sclerenchyma does not have intercellular spaces.
Nature of Cell
Parenchyma Cells
The nature of the Parenchyma cell is living.
Collenchyma Cells
Collenchyma cells are also living cells.
Sclerenchyma Cells
But, on the contrary, sclerenchyma are dead cells.
Function
Parenchyma Cells
Parenchymata perform photosynthesis and also aid in gaseous exchange.
Collenchyma Cells
Collenchyma cells bring flexibility to plants and provide mechanical support against wind and other factors.
Sclerenchyma Cells
They give plants mechanical strength and help to transport food and water via xylem and phloem.
The Bottom Line
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells are present in kinds of plants, including angiosperms and gymnosperms. Parenchyma cells play their role in gaseous exchange and photosynthesis, while collenchyma cells offer mechanical support and flexibility. At the same time, sclerenchyma cells contribute to food transport. The main difference between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma is their cell wall structure and composition. Parenchyma cell walls are thin, whereas sclerenchyma cells are thick, and talking about the sclerenchyma , it is thicker.
FAQs
What is the difference between parenchyma and collenchyma?
Parenchyma and collenchyma are living cells in the plant body that support the plant. Parenchyma cells have a thin cellulose cell wall, while collenchyma cells comprise pectin and hemicellulose.
What is the difference between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma, based on their cell wall?
Parenchyma cell walls are thin and comprise cellulose, while collenchyma cells have localized thickening. Contrarily, sclerenchyma cell walls are made of lignin and have thick cell walls.
What is the function of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma?
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma contribute to gaseous exchange, food storage, elasticity, mechanical support, and transport of nutrients. Collenchyma cells also provide structural support in young plants.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.