The fascinating world of plants has always been intriguing. These incredible species and subspecies have amazed us for centuries with their many diverse features. One such amazing feature of plants is the ability to get energy through sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. A plant cell is responsible for the growth and development of the entire plant body.
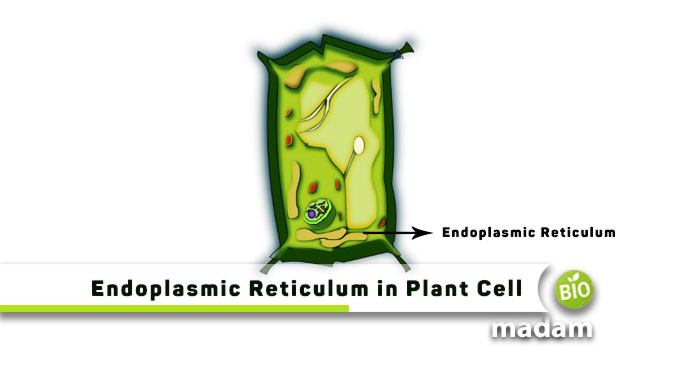
Just like animals, plant cells also have many specialized organelles. Most of the organelles between the two are the same however there might be some differences. People usually wonder ‘’do plant cells have endoplasmic reticulum?’’ And the simple answer to it is, “Yes!” plants do have endoplasmic reticulum, just like any other eukaryotic cell, and that is why we are here to help you more with it.
What is Endoplasmic Reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a cell organelle found in all eukaryotic cells, consisting of a continuous membrane system. This membrane system forms a series of flattened sacs in the cytoplasm of the cells. The main functions of the endoplasmic reticulum include the synthesis, modification, transport, and folding of proteins. The endoplasmic reticulum found in animal cells constitutes half of the membranous content of the cell.
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
Depending upon the physical and functional characteristics, the endoplasmic reticulum is divided into two types:
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
Do Plant Cells have Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Plant cells do have an endoplasmic reticulum. They have both types of ER present in them, smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum. Both of these endoplasmic reticula perform their own distinct functions. Rough ER has several ribosomes attached to them that are responsible for protein synthesis. Smooth ER does not have ribosomes attached to them but is responsible for lipid synthesis.
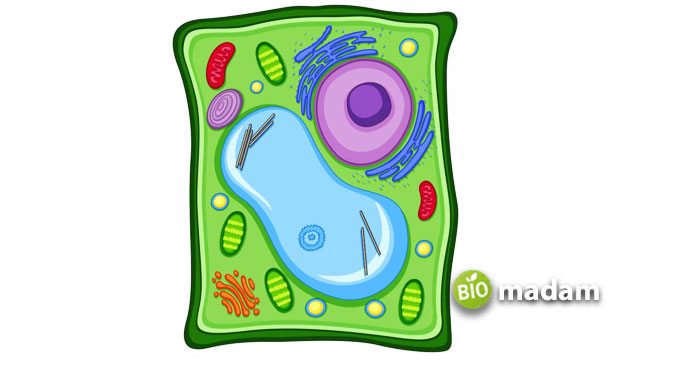
Other Organelles in Plant Cells
Plant cells have several organelles in them, responsible for performing a variety of functions for the development and growth of the plant. Some of the major organelles found in the plant cell are enlisted here:
- Nucleolus
- Nucleus
- Ribosome
- Vesicle
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- Cytoskeleton
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
- Mitochondria
- Vacuole
- Cytosol
- Lysosome
- Centriole
Function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum in Plant Cells
As the name suggests, RER has a rough appearance. This is due to the presence of ribosomes on their outer surface. These ribosomes are specialized for the synthesis of proteins. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is located adjacent to the nucleus and its membrane is linked to the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. The proteins synthesized by the RER have different roles at different locations within the cell. Some types of proteins remain within the RER while some others are sent to the Golgi apparatus. The proteins which are released from the Golgi apparatus are then sent to the lysosomes.
The rough endoplasmic reticulum can easily participate in protein processing as it lies close to the nucleus. When there is any problem in protein synthesis, the RER sends a signal to the nucleus that solves the problems in protein folding and regulates the overall rate of protein translation.
Function of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum in Plant Cells
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum lacks ribosomes and has a rather smooth appearance. Its function differs from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Instead of the synthesis of proteins, smooth ER is responsible for the synthesis and storage of lipids, such as cholesterol and phospholipids, and in the synthesis of hormones. These lipids are used in the production of cell membranes.
The Bottom Line
Plant cells have different organelles that are specialized to perform different functions. These functions help in the growth and development of the plant. Plant cells have a specialized organelle called ‘’endoplasmic reticulum.’’ It is found in all eukaryotic cells including animal and plant cells. It is a continuous membrane system consisting of flattened sacs. There are two types of ER present in the plant, smooth ER and rough ER. Rough ER has plenty of ribosomes attached to it and is responsible for protein synthesis. Smooth ER lacks ribosomes and is involved in the synthesis and storage of lipids and hormones.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are a few frequently asked questions about the endoplasmic reticulum:
When and who discovered the endoplasmic reticulum?
In 1902, the endoplasmic reticulum was first discovered by Emilio Veratti as sarcoplasmic reticulum in the muscle fibers. Almost 50 years later, a new organelle, endoplasmic reticulum was first found and visualized through electron microscopy by Keith Porter.
What is the difference between smooth ER and rough ER?
The main difference between smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum is the presence or absence of ribosomes. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to them whereas smooth ER does not have ribosomes attached to them.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum in animal cells?
The functions of the endoplasmic reticulum in animal cells are the same as in plant cells. It is involved in the synthesis of proteins, lipids, and hormones. It is also responsible for the removal and detoxification of waste from the body. ER is also involved in the regulation of calcium ion concentration in the skeletal muscles.
Do all plant cells have rough endoplasmic reticulum?
All plant cells have rough endoplasmic reticulum. It is distributed throughout the cell but their density is higher near the nucleus and Golgi apparatus.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.