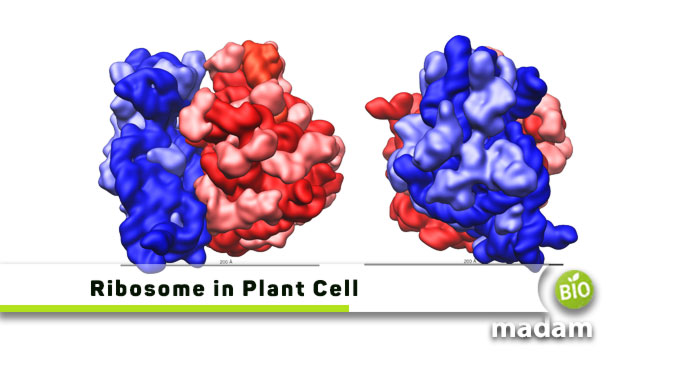
Ribosomes are an important part of the plant cell besides the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. They have a pivotal role in the production of different proteins in the body. You may also call them the factories of the cell as they produce amino acids that contribute to various tissues and organs. Keep reading to learn the structure and function of ribosomes in the plant cell.
What are Ribosomes?
Ribosomes are complex molecular structures within the cell responsible for producing amino acids. These amino acids form various protein structures through translation. Ribosomes are essential to life and are found in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Ribosomes are a combination of proteins and a specific type of RNA, i.e., ribosomal RNA, to make complex structures called ribonucleoproteins. The structure has around 62% RNA, and the remaining 38% are proteins. The organelle comprises a larger and a smaller subunit. The smaller subunit enables the binding of mRNA for decoding, followed by the addition of the amino acids to the larger subunit. The interaction between proteins and rRNA leads to the formation of this structure based on two subunits. The size of ribosomes varies between eukaryotes and prokaryotes as a result of the difference between the size of subunits. Prokaryotic ribosomes are the 70S with 50S and 30S subunits. At the same time, eukaryotic ribosomes are the 80S with larger subunits of 60S and smaller of 40S.
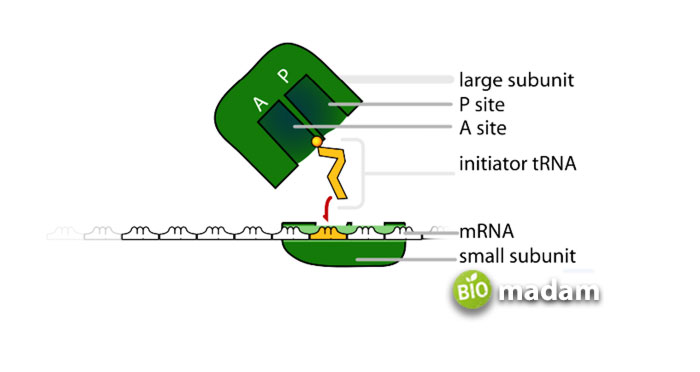
They are either scattered in the cytoplasm or found attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Both these ribosomes look the same and perform the same function – protein synthesis.
Function of Ribosomes
The main function of ribosomes is the production of proteins in the body through translation.
The transcription of DNA to mRNA leads to the formation of proteins by reading the information present in the mRNA. This process is known as translation. mRNA is single-stranded, and the base order present in their structure is complementary to the specific protein. Every mRNA ensures that the amino acids are formed and added in the correct order to a protein chain as it forms. Each amino acid is depicted through a codon along the mRNA molecules. UAA is an mRNA signal to stop the process of protein translation. It is also known as a stop codon.
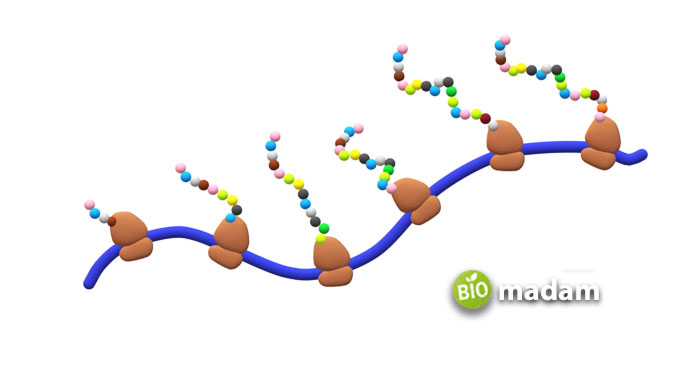
Furthermore, the tRNA molecules match the amino acids with relevant codons in mRNA. They comprise two ends where each binds to a particular amino acid. The other end of the tRNA binds to an appropriate mRNA codon. The tRNAs are also responsible for carrying amino acids to the ribosomes to ensure they join with the suitable codons. The synthesized amino acids then join together to form long protein chains. The tRNA and ribosomes move along the mRNA, and the resulting protein chain may have a variety of amino acids depending on the type of protein produced by the ribosomes and RNA combined.
The Bottom Line
Ribosomes play an integral part in plant cells producing proteins that form different tissues within the plant. They are present on the endoplasmic reticulum adjacent to the nucleus in plant cells. Alternatively, you may also see them dispersed in the cytoplasm. The production of proteins is the fundamental function of ribosomes in plant cells. They translate the mRNA code into an amino acid sequence that joins to form long chains of proteins essential for plant growth.
FAQs
How many ribosomes are in a cell?
Different eukaryotic cells have a large number of ribosomes counting to as many as 10 million in a mammalian cell. They use their energy to produce proteins.
Who discovered ribosomes?
Ribosomes were discovered by George E. Palade in 1955 when he saw these small particles in the cytoplasm and also identified their presence on the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the size of the ribosome?
Ribosomes range between 20 and 30 nm in size in different prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. They all comprise large and smaller subunits.
What color is a ribosome?
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic organelles have specific colors. Ribosomes appear blue in color under the microscope. Cell membrane color is red while lysosomes look pink.
What shape is a ribosome?
Ribosomes are small spherical organelles in the cell when seen under an electron microscope. Their shape is spherical and flattened with a size of 20 nm to 30 nm.
Why are ribosomes in all cells?
Ribosomes are present in all cells as they are responsible for producing proteins. They build proteins by connecting amino acids together by decoding the instructions in the mRNA.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.