Photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and fermentation are often used together to explain energy production in different organisms. Fermentation and cellular respiration are similar and different to each other in specific ways. Fermentation refers to the breakdown of material by yeast, bacteria, or other microorganism. On the other hand, cellular respiration converts glucose into usable energy for biochemical processes. Organisms in our ecosystems perform fermentation and cellular respiration. Let’s tell you all the differences between fermentation and cellular respiration.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Fermentation | Cellular Respiration |
| Definition | Breakdown by yeast or bacteria | Energy production by oxidizing food |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Function | Supplements the slower ATP production | Produces energy to facilitate cellular processes |
| Location | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm & mitochondria |
| Types | Ethanol fermentation & lactic acid fermentation | Aerobic and anaerobic |
| ATP Production | Two | Thirty six |
| Speed | Slow | Fast |
| Involved Molecules | Methane and Sulphur | Oxygen |
| Substrate Breakdown | Incomplete | Complete |
| NAD+ Regeneration | No ATPs | Three ATPs |
| End Products | Ethanol, lactic acid, CO2, and H2 gas | Inorganic molecules, water, and carbon dioxide |
What is Fermentation?
Fermentation refers to the breakdown of organic material by microorganisms like yeast. Besides yeast, some bacteria and parasites also contribute to fermentation. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms carry out fermentation to produce ATP without oxygen. It involves the metabolism of sugars to produce effervescent fatty acids. Fermentation is an exothermic reaction resulting in heat and effervescence. The process takes place in the cytosol of cytoplasm.
It may happen in the muscles in stress conditions due to a restricted supply of oxygen that eventually leads to the formation of lactic acid, causing muscle cramps. Fermentation also plays a role in the synthesis of ethanol in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol acts as an energy source for petrol gasoline.
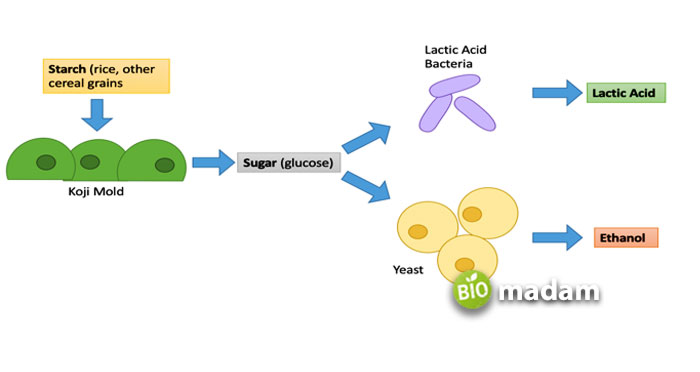
Mechanism of Fermentation
Fermentation comprises glycolysis followed by partial oxidation of pyruvate. The process of glycolysis is the same in both, whereas pyruvate oxidation differs. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate and generates two ATPs. Furthermore, two molecules of NADH are produced by obtaining electrons from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
Types of Fermentation
Fermentation is generally of two types: ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Ethanol Fermentation
Ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast without the utilization of archaea or bacteria. The yeast exhibiting this type of fermentation is known as facultative anaerobes. Pyruvate molecules are decarboxylated into acetaldehyde. The hydrogen atoms of the NADH convert acetaldehyde into ethanol. It results in the release of carbon dioxide that appears as effervescence.
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation takes place in gram positive bacteria. Other organisms, like animals, also produce lactic acid in their muscles in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation converts pyruvate into lactic acid, which later oxidizes into lactate.
What is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is common in all organisms, whether autotrophs or heterotrophs. As the name indicates, it refers to the respiration process at the cellular level. It combines metabolic reactions within the cell to convert biochemical energy from food into ATPs. The process takes place within the mitochondria in different eukaryotic cells. The mitochondria contain the enzymes acting as catalysts to carry out the process.
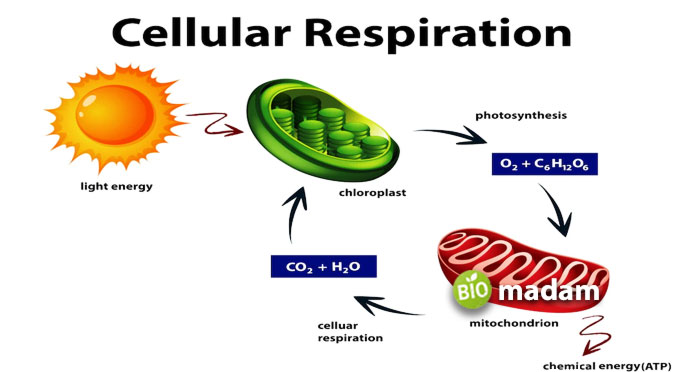
Cellular Respiration Mechanism
Cellular respiration occurs through the combination of oxygen with macronutrients obtained through food. They divert the chemical energy in the food into biochemical activities essential for the sustenance of life. This process is divided into three stages or parts: glycolysis, TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis is the first step of the cellular respiration process. It is a sequence of 10 biochemical reactions in the cell to break down glucose into two pyruvic acid molecules. The breakdown of glucose, fats, other carbohydrates, and proteins is stored in ATP. This process also converts NAD to NADH, followed by the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A in the mitochondria.
The acetyl coenzyme A enters the TCA cycle comprising eight steps catalyzed by eight different enzymes. These steps produce energy that NAD and FAD capture and convert into ATPs. FAD and NAD molecules are reduced to NADH and FADH molecules. They provide energy to the next step of cellular respiration. The TCA cycle is also known as the Krebs cycle.
Oxidative phosphorylation is the last step of the process. Hydrogen atoms removed from NADH and FADH offer a pair of electrons that reduce one atom of oxygen to produce water. This transfer of electrons leads to the production of three ATP molecules. It conserves the energy from the food to carry out cellular functions. As this process involves the transfer of electrons, it is also called the electron transport chain.
Types of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration can be categorized into two types: Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen to produce energy. It is common in plants and animal cells and expressed through:
Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen (6O2) → Carbon dioxide (6CO2) + Water (6H2O) + Energy (ATP)
Anaerobic Respiration
Unlike fermentation, anaerobic respiration refers to a process that does not require oxygen. Thus, anaerobic respiration is the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen. It also leads to energy liberation. The following equation can help us understand it.
Glucose (C6H12O6) → Alcohol 2(C2H5OH) + Carbon dioxide 2(CO2) + Energy (ATP)
Similarities Between Fermentation and Cellular Respiration
- Fermentation and respiration are cellular processes.
- They lead to the production of energy in the form of ATPs.
- Both processes can occur in the absence of oxygen.
Differences Between Fermentation and Cellular Respiration
Definition
Fermentation
Fermentation refers to breaking organic substances like glucose by yeast and bacteria.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration, on the other hand, is the production of energy by oxidizing food to release water and carbon dioxide as by-products.
Function
Fermentation
Fermentation helps supplement the slower ATP production in cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
While cellular respiration produces energy to facilitate cellular processes within the cells.
Efficiency
Fermentation
Fermentation is less efficient in the production of ATPs.
Cellular Respiration
Contrarily, cellular respiration is more efficient in generating ATPs.
Location
Fermentation
Fermentation takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Cellular Respiration
On the other hand, cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of a plant or animal cell.
Types
Fermentation
The two types of fermentation are ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
Cellular Respiration
At the same time, cellular respiration can either be aerobic or anaerobic.
ATPs Produced
Fermentation
This process produces 2 ATP molecules on the breakdown of glucose molecules.
Cellular Respiration
Whereas cellular respiration gives rise to 36 ATPs as a result of glycolysis.
Speed of Reaction
Fermentation
Fermentation is a slower process compared to cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
On the contrary, cellular respiration produces energy faster.
Involved Molecules
Fermentation
Fermentation uses inorganic ions like methane and sulfur to produce ATP.
Cellular Respiration
Meanwhile, cellular respiration uses oxygen as the electron acceptor in the process.
Substrate Breakdown
Fermentation
Bacteria and yeast do not completely break down the substrate.
Cellular Respiration
Conversely, cellular respiration leads to the complete breakdown of the glucose molecule.
NAD+ Production
Fermentation
The regeneration of NAD+ does not produce ATPs during fermentation.
Cellular Respiration
However, NAD+ regeneration in cellular respiration gives rise to three ATPs.
End Products
Fermentation
The end products in ethanol and lactic acid fermentation are different from each other. Ethanol fermentation produces ethanol and carbon dioxide, while lactic acid fermentation generates lactic acid.
Cellular Respiration
Alternatively, cellular respiration produces inorganic molecules, water, and carbon dioxide as end products.
The Bottom Line
Fermentation and cellular respiration are the naturally occurring processes in our biome and ecosystem. Fermentation occurs through yeast and bacteria, while cellular respiration occurs in higher organisms. The main difference between fermentation and cellular respiration is the production of lactic acid and ethanol in fermentation. Fermentation is a faster process yet produces only 2 ATP. On the other hand, cellular respiration takes more time and generates 36 ATPs. The produced energy is used to facilitate different biochemical processes within the body.
FAQs
What is the main difference between fermentation and cellular respiration starting compounds?
NADH does not go through oxidative phosphorylation in fermentation to synthesize ATPs. However, cellular respiration produces 3 ATPs per NADH molecule to generate energy.
What is fermentation simple explanation?
Unlike other processes, such as aerobic or anaerobic respiration, fermentation is the breakdown of a substance like glucose into simpler molecules. Bacteria and yeast typically carry out fermentation.
What is the major difference between respiration and anaerobic respiration?
Cellular respiration typically uses oxygen in the electron transport chain. Meanwhile, anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.