Recently updated on October 5th, 2023 at 05:59 am
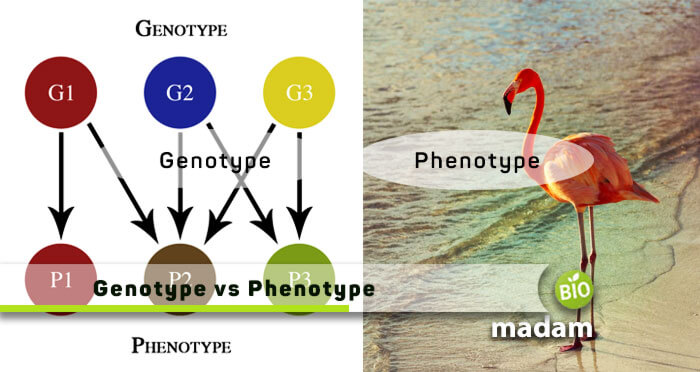
While genotype and phenotype sound alike, they are not the same. The name “Genotype” indicates the type of genes, whereas Pheno in “Phenotype” refers to appearance. Both of them are significantly important when it comes to studying the characteristics and traits of an organism. Phenotype and genotype are critical factors of biological studies and help understand different aspects of an organism’s personality and hereditary sequence.
Let’s have a look at phenotype and genotype definition and their differences with interesting examples for better understanding.
What is a Genotype?
A genotype is simply defined as the set of genes an organism possesses. Genes are basic hereditary units that carry the information of an organism’s features through DNA. The characteristics sometimes express themselves through a single gene or multiple genes. Genes exhibiting the same characteristic are called alleles.
A genotype can also be defined as the set of an organism’s alleles for a particular gene.
Genotype Example
One of the most common examples of genotype in human beings is eye color. Eye color has different alleles like blue and brown. Brown eye color is the result of dominant allele, whereas blue color shows recessive allele. It means that if one parent has a brown allele and one has a blue allele passed down to the offspring, their eye color will be brown. The child will have blue eyes when both the parents have a blue eye color gene.
Height is also an example of a genotype but is influenced by multiple genetic variants. Up to 700 variants have been identified by researchers. Isn’t it amazing!
What is a Phenotype?
The phenotype of an organism defines its observable characteristics. They are not solely dependent on genes, and environmental factors play a major role in determining the phenotype.
A phenotype can also be expressed as the observable result of genotypes from the parents and epigenetic changes.
Phenotype Example
Hair volume and length can be considered an example of a phenotype. You see many people telling that they do not do any haircare and have beautiful hair genetically. Yes, genes play a part in determining how your hair will be (depending on your mother and father’s), yet proper hair care also contributes to keeping them healthy. People who take care of their hair have gorgeous hair for a longer period than those who neglect it.
Other phenotype examples include skin complexion, hair color, and body pigment of flamingos.

Interlinkage between Genotype and Phenotype
To explain in easy words, a phenotype is a characteristic that expresses itself, whereas the cause of that character (DNA) is the genotype.
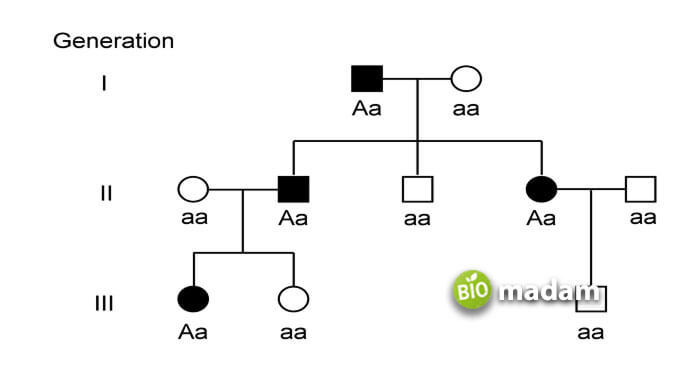
One of the common examples we see around us is “attached” and “free” lobes. Humans are seen to have two different types of ear lobes. One is attached to the skin on the face, while the other hangs freely.
Free earlobes are a dominant trait and expressed as “E,” while attached earlobes are recessive and given as “e.” If a child receives “Ee” or “EE” from their parents, they get unattached earlobes, and “ee” results in attached earlobes.

Differences between Genotype and Phenotype
Definition
Genotype
Genotype defines the genetic makeup of an organism determined by the parents’ genes that stays the same throughout their life.
Phenotype
Phenotype is the set of visible characteristics of an organism. It may differ during the life of an individual.
Inheritance
Genotype
Genotype passes from the parents to the offspring. The child gets characteristics based on genotypes from both parents.
Phenotype
Phenotype is not entirely inherited from generation to generation.
Environmental Factors
Genotype
Environmental factors do not directly influence the genotype as they come from parents.
Phenotype
Phenotype is affected by the genetic makeup as well as environmental conditions. For example, your skin gets darker (than your genotype determination) when exposed to UV rays for a long time.
Constituents
Genotype
Genotype consists of genes that contain the DNA to determine a person’s physical and mental traits.
Phenotype
Phenotype comprises numerous expressable traits like a person’s behavior, body structure, etc.
Determinants
Genotype
The genotype of a person or animal is determined through gene testing like DNA sequencing, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), and RELP.
Phenotype
Phenotypes can be easily observed by considering physical appearance.
Expression
Genotype
Genotypes are expressed as a combination of alleles like Aa, BB, etc.
Phenotype
Phenotypes are expressed as observable features like blood group, hair color, etc.
Examples
Genotype
Examples of genotype include Ee for earlobes, BB for eyes, Tt for height, and β°β° for thalassemia major.
Phenotype
Examples of the phenotype are eye color, hair color, melanin production, the color of flamingos, etc.
FAQs
Why is genotype important?
Usually, biologists and genetic engineers use genetic information to study organisms and their traits. It helps them determine recessive and dominant traits. Scientists are working to prevent hereditary diseases by finding appropriate solutions.
Are phenotypic changes permanent?
No, phenotypic changes are not always permanent and may change throughout a person’s lifetime.
How to determine one’s genotype?
You can determine an individual’s genotype through genetic testing. Different genetic tests like RELP and PCR are carried out for varying studies.
How do you test for phenotypic plasticity?
You can determine the phenotypic plasticity by using ANOVA (analysis of variance). It is a statistical procedure that quantifies phenotypic plasticity by evaluating a set of genotypes and environments to study the phenotype.
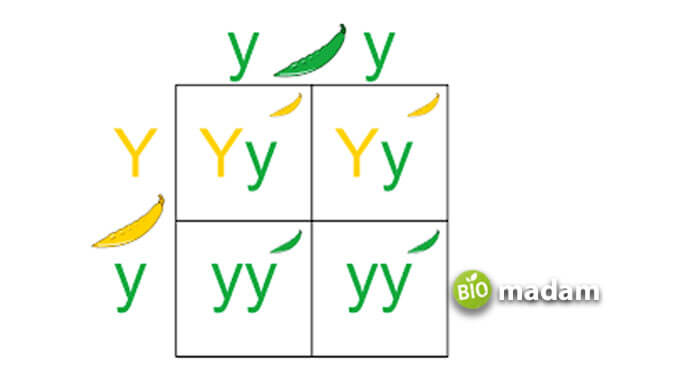
What is a Punnet square?
A Punnet square lets you determine the traits of the next generation by studying the genotype of parents considering dominant and recessive genes.
The Bottom Line
Phenotype and genotype are both very important while studying the hereditary traits and behavior of organisms. They do not only help researchers find out hereditary features but also genetic diseases and their patterns. Understanding the genotype and phenotype also enables biologists to improve cultivation by creating new breeds of the same species, but with improved characteristics. While genotype helps alter the genetic makeup through engineering, phenotype shows the results. Genotype, however, is not altered by environmental factors, whereas phenotype is influenced by the environment, like changes in skin tone on exposure to UV rays.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.