DNA sequencing alludes to different methods of examining the arrangement of nucleotide bases in DNA. These bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Several researchers in the 1970s worked on the sequel of DNA by utilizing some laboratory techniques that depend on two-dimensional chromatography. These are the chemical method (Maxam Gilbert Method) and the chain termination method (Sanger Dideoxy Method). Today, we will discuss all these terminologies and how do they help in DNA sequencing.
Maxam Gilbert Method & Sanger Dideoxy Method – Difference in Basic Principles
Both terms are generally responsible for determining the nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule; however, there are differences in their principles. Maxam Gilbert’s arrangement works by the partial, nucleobase-specific chemical amendments of DNA sequencing and cleavage of its backbone at points next to the reformed nucleotides. In comparison, the Sanger Dideoxy sequencing is the chain termination procedure that interferes with the DNA elongation by involving dideoxynucleotides in the sequencing. Maxam Gilbert isn’t used nowadays because of its hazardous chemicals, such as hydrazine and radioactive materials. On the other hand, Sanger Dideoxy uses comparatively fewer dangerous chemicals.
Let’s step forward to get an overview of both the DNA sequencing methods:
Maxam Gilbert Method of DNA Sequencing
This method is the first and oldest method of DNA sequencing, introduced by American molecular biologists during the 1970s. Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbert analyzed the DNA sequencing depending on chemical amendments of the DNA and its cleavage at particular base points.
Why Do We Call It Chemical Method?
The Maxam Gilbert DNA sequencing requires a large amount of radioactive labeling at one point and purification of the DNA fragments to be arranged at the other point. Therefore, due to the immense usage of chemicals in the procedure, the method is also called Chemical Method.
Procedure
- The foremost step in Maxam Gilbert sequencing is the denaturation of DNA into its single strand. It is further labeled with gamma-32P at the 5′ end.
- Four test tubes are allotted to four nucleotide bases, called Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine. The primary purpose of this step is to apply a high-percentage gel (polyacrylamide) on the prepared bases to distinguish the fragment sizes. The radioactive tags in the procedure visualize these fragments.
- Only the bases with 32-P will remain after the completion of electrophoresis and autoradiography.
- This method of DNA sequencing lost its popularity due to its time-consuming behaviour. Moreover, it was challenging to handle the toxic substances used.
Importance of Maxam Gilbert Sequencing
The process holds significant importance due to its sensitivity and specificity, leading to great distinction in nucleotide bases. Although being specific, it still consumes a couple of days to sequence some hundreds of bases. Maxam Gilbert utilizes hydrazine (a neurotoxin) and also other radioactive elements to series the DNA through radioactive decay.
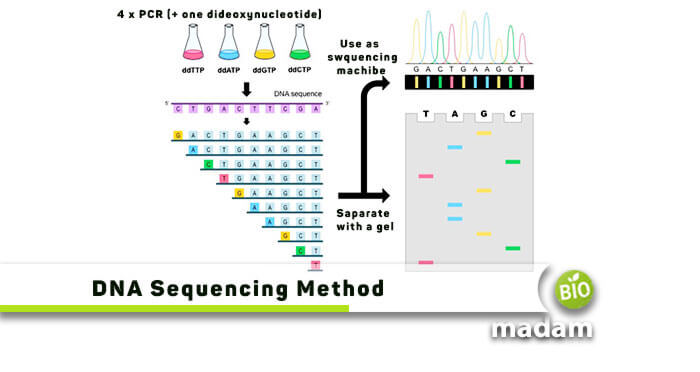
Sanger Dideoxy Method of DNA Sequencing
A scientist named Frederick Sanger, in 1977, introduced a traditional DNA sequencing method which is the most used technique in biochemistry. This methodology is also called as Dideoxy method or the chain termination method.
Why Do We Call It Dideoxy Method?
Sanger DNA sequencing usually depends on incorporating the chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) by utilizing DNA polymerases through in vitro DNA replication. These ddNTPs naturally are deficit of the 3’-OH group accountable for forming a phosphodiester bond with the nucleotide. Due to this deficiency, the polymerase enzyme ceases the elongation of DNA that was to be incorporated by modified ddNTP. Hence, it is termed as Dideoxy Method.
Reason for Chain Termination
There is a lack of OH group that can attach to the next nucleotide for chain elongation. That is why this ddTTP is called Chain Termination Reaction.
Procedure
- The DNA sample is initially divided into four distinct sequencing reactions ddCTP, ddATP, ddTTP, and ddGTP.
- DNA polymerase adds ddNTPs instead of the normal dNTPs as a substrate and adds them to the primer. This primer is hydrogen-bonded to the 3′ end of the DNA that is to be sequenced.
- Denaturation of DNA template occurs through heating which is further cooled, and the primer can then bind to the single-stranded template.
- The temperature rises after the primers are attached again, allowing the DNA polymerase enzyme to synthesize new DNA, starting from the primer. DNA polymerase keeps on adding nucleotide chain until the dideoxy appears, ultimately ending the strand elongation.
- At the end of the incubation period, capillary Gel Electrophoresis separates the fragments, where the short pieces move quickly, and the long ones move slowly. The resolution is so good that one nucleotide difference is enough to separate that strand from the next shorter and longer strands.
- Each of the four dideoxynucleotides reports a different color when illuminated by a laser beam, and an automatic scanner provides a printout of that specific sequence.
Importance of Sanger Dideoxy Sequencing
The Sanger technique can be used in RNA as well as DNA sequencing. If you want to sequence RNA, a single-stranded DNA copy is made using RNA as a template by an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. Various sized DNA fragments are generated for the Sanger type sequence in the presence of ddNTPs by making single-strand DNA. Although it doesn’t utilize many hazardous chemicals, the process is still a sensitive one.
Cost of DNA Sequencing
According to CNBC, it shows the cost of sequencing a genome diverged drastically in 2008, falling from almost $10 million to close to $1,000 today.
The first human genome took $2.7 billion and almost 15 years to complete. Now, according to Cowen analyst Doug Schenkel, genome sequencing and analysis cost is around $1,400.
DNA Sequencing Services
- Molecular biology labs in the USA provide DNA sequence services. North America offers high-quality services by trained staff.
- GENEWIZ also provides services of Sanger sequencing within 24 hours.
- Speedy sequence DNA provides customer services of DNA sequencing at different costs.
- Furthermore, Speedyseq DNA sequencing in 1 reaction price is $7.50.
- PCR clean–up, through different types of PCR, for Sanger sequencing in 1 sample is $5.00.
Next-Generation Sequencing

NGS has revolutionized genomic research in recent years. By using NGS, one can sequence a human genome in a single day. It is also known as high-throughput sequencing, a term used to describe several different modern techniques, such as:
- Solid sequencing
- Roche 454 sequencing
- Iron torrent; proton / PGM sequencing
- Illumine sequencing
Conclusion
In the process, DNA sequencing attained the right place in a short time by being an affordable and fast methodology. Besides identifying several microbes, for instance, bacteria and viruses, in the laboratory, it can also separate the segments of genes and DNA. Scientists mainly implement the Sanger Dideoxy Method of DNA sequencing because it comparatively engages less hazardous substances.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.