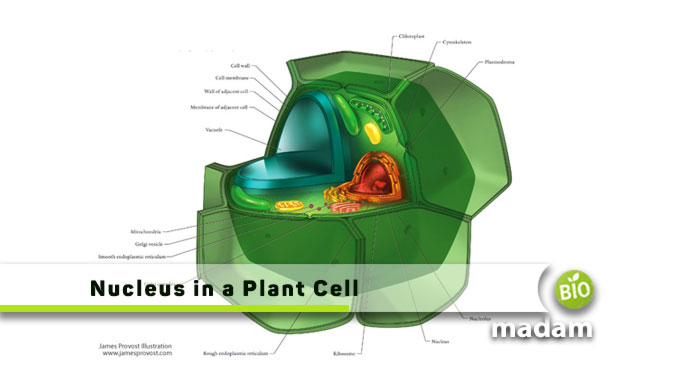
Plants and animals comprise different types of eukaryotic cells, and are thus quite similar to each other. However, the structure of the plant cell varies slightly from the animal cell. Vacuoles present in animal cells are smaller while the plant vacuole covers a large part of the cell. Thus, it also alters the location and shape of the nucleus within the cell. Keep reading to learn everything about the function of the nucleus within the plant cell.
What is the Nucleus?
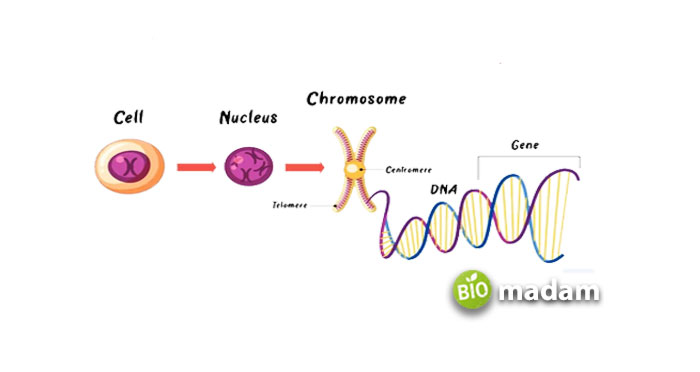
The nucleus is one of the fundamental components of the cell. It is a large organelle that protects the genetic information in the form of DNA and chromosomes. The DNA contains all information about the characteristics of the organism. It also accounts for the information required for the synthesis of proteins in the cell. Besides the nucleus, some DNA is also present in the mitochondria. Yet, the majority of the genetic material is found in the nucleus of the plant cell.
Location of Nucleus
The nucleus in animals resides almost in the center of the cell in the cytoplasm. On the other hand, plants do not have a nucleus in the middle due to the presence of a large vacuole. It pushes the nucleus, along with other organelles to a side. Thus, the nucleus is present towards the side of the cell, surrounded by the other organelles like smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum in animal cells.
Structure of Nucleus in Plant Cell
Plant nuclei may have an oblong shape compared to the spherical nucleus in the animal cell. While the true shape of the nucleus is spherical, the pressure exerted by the vacuole may not allow it to maintain the shape. Thus, the nucleus takes up an oblong shape.
The nucleus is a double-membrane-bound organelle. The membrane covering the nucleus is called the nucleus envelope, which is semi-permeable. It only allows small molecules and different types of proteins of less than 50kd to move through it. Some specific macromolecules need to synthesize DNA and RNA and also move into the nucleus.
The semi-permeability allows the nucleus to maintain a separate environment for the DNA. The outer membrane of the nucleus is exposed to the cytoplasm whereas the inner membrane is connected to the nuclear lamina. The nuclear lamina is a nuclear framework within the nucleus that enables it to maintain its shape. Moreover, a small structure called the nucleolus is present in the nucleus that manufactures ribosomal components.
Function of Nucleus in Plant Cell
The nucleus in the plant cell is of significant importance as it contributes to various cellular functions. These functions are critical to growth, development, and reproduction.
Protects the DNA
The main function of the nucleus in the plant cell is the protection of the DNA and genes. The genetic material is enclosed in the nucleus and contributes to the production of different components in the cell.
Ribosome Production
The nuclear membrane of a plant nucleus allows the entry of molecules into the nucleus essential for the production of ribosomal components. Some substances also contribute to the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
Multiplication
The nucleus is the main site for the multiplication and division of the genetic material through mitosis and meiosis. The DNA forms chromosomes that ensure equal division of genetic material between the daughter cells.
Enzyme Regulation
Besides its activity in producing and regulating genetic activity, the nucleus controls all cellular processes by managing the enzymes required for cellular activities. They include metabolism, growth, protein synthesis, and reproduction. Thus, the nucleus is also known as the brain of the cell.
The Bottom Line
Plant cell nucleus performs the same function as animal cells. However, it differs slightly in its location and structure. The presence of a large vacuole pushes the nucleus to a side in the plant cell. Thus, the exerted pressure may also alter the spherical shape to an oblong one. The nucleus plays a major role in protecting the genetic material and contributes to enzyme regulation. It also manages activities like growth, metabolism, and reproduction. That is why the nucleus is also known as the brain of the cell.
FAQs
Do plant cells need a nucleus?
The nucleus is essential to all eukaryotic organisms including plants and animals as it contains genetic information. The nucleus contributes to all cellular activities within the cell including growth and reproduction.
Is the nucleolus only in plant cells?
The small spot observed within the nucleus, the nucleolus, is a component of all eukaryotic cells including animals, plants, fungi, and protists. It plays a role in RNA synthesis that contributes to the production of ribosomes.
What is a plant cell without a nucleus called?
Cells without a nucleus are called anucleated cells. Sieve tube cells in plants do not have a nucleus. They are the only living cells in plants without a nucleus.
Do dead cells have a nucleus?
Dead cells do not have a nucleus as the death of the cell is indicated by the disintegration of the cell including the nucleus. The fragments of the dead cells are often engulfed by the neighboring cells.
Which cells live after death?
Cell death refers to the cessation of the function of a cell completely. However, the skeletal muscle stem cells stay alive in the body for as many as 17 days after the death of a person.
Who discovered the nucleus?
Robert Brown first identified the nucleus in the cell in 1831. It was the first cell organelle to be discovered and studied.

The Biomadam Content Team develops and manages educational and informational articles published on Biomadam. Content is prepared using standard reference materials and follows internal editorial guidelines to ensure clarity and consistency.