Recently updated on October 5th, 2023 at 06:20 am
Plants are composed of highly organized tissues that make up the structure of the plant. All organs of the plant, including different types of leaves, stem, and roots have all three tissues present. Different tissues like ground, dermal, and vascular tissues make up the plant body together. They are specialized tissues and are involved in specific functions. Let’s explain the functions of vascular tissues in plants for better understanding.
What is Vascular Tissue in Plants?
Vascular tissues are one of the types of tissues found in plants. They are made of multiple cells and enable the transport of materials through the plant for essential processes. They are only found in vascular plants, whereas nonvascular plants like mosses and algae do not have vascular tissues, restricting the transport of water and nutrients.
Types of Vascular Tissues
Vascular tissues in vascular plants are of two types
- Xylem
- Phloem
They are both examples of vascular tissues in plants and are involved in transporting material through the plant to enable photosynthesis. Yet, their function is not entirely the same.
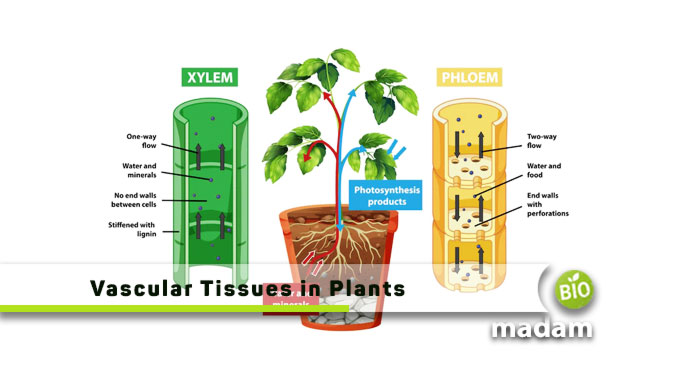
What is Xylem?
The xylem is an essential part of the plant structure as water is vital for the growth of plants. It is composed of tracheids and vessel elements. They are elongated tubular cells and help in conducting water from the roots. Tracheids are a part of all vascular plants, including angiosperms and gymnosperms, but vessel elements are present only in angiosperms. You may be surprised to know that tracheids and vessel elements are made of dead cells.
Function of Xylem
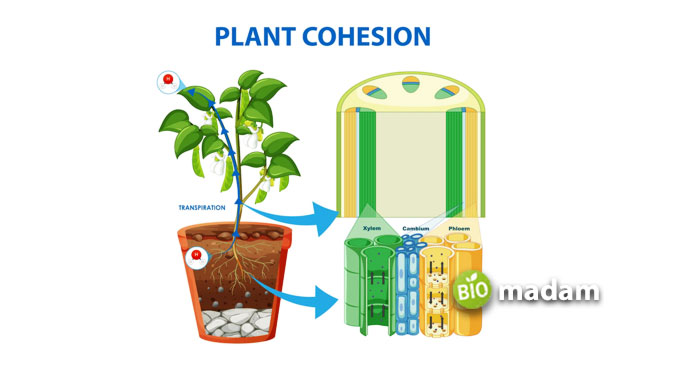
Xylem transports water and nutrients from the roots to various plant parts. The roots absorb water and generate a positive pressure, allowing the leaves to pull water on transpiration. This process makes the transport of water possible to different parts of the plant. Other than transpiration, evaporation also takes place in green plants.
What is Phloem?
Phloem is the second type of vascular tissue present in plants. Opposed to Xylem, Phloem is responsible for transporting materials to the roots. While the xylem is composed of dead cells, the phloem is made of living parenchyma and sclerenchyma cells. The structure consists of sieve cells and a sieve plate that helps it perform the transport of material. Phloem obtains water from plants to facilitate the process.
Function of Phloem
As we mentioned, phloem is involved in the transport of material to the roots. But what kind of nutrients does phloem carry?
Phloem is responsible for the transport of sugars produced by photosynthesis to the plant’s roots. The sieve cells and sieve plate enables nutrient transfer from the leaves and other parts to the sink cells in the leaves.
FAQs
What are vascular plants known as?
Vascular plants are typically known as tracheophytes as they comprise tracheids.
Why is xylem made of dead cells, but phloem is made of living cells?
The main reason for phloem consisting of living cells is their active transport. Phloem is involved in the active transport of sugars, and the cells must be alive to perform the functions smoothly. However, the xylem transports water and nutrients, which easily seep through the tubules and do not need living cells in the structure.
How do nonvascular plants get water?
Nonvascular plants differ from vascular plants and do not have xylem or phloem to transport water and nutrients from the root to other plant parts and vice versa. Instead, they transport materials through passive osmosis using leaflike scales or rhizoids. Microscopic openings on the surface of the leaves of these plants enable excretion. Due to the absence of vascular tissues, nonvascular plants do not attain the same height as vascular plants.
What is the vascular tissue function in humans?
The vascular tissues in humans are different from plants. Contrary to the xylem and phloem in plants, humans have a network of blood vessels (veins, arteries, and capillaries) that perform blood circulatory functions in the body. They transport blood to and fro different parts of the body.
The Bottom Line
Vascular plants are an important part of the ecosystem. They are composed of two types of vascular tissues – xylem and phloem. They both perform their functions in a specialized manner and contribute to the growth of the plant. Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to other plant parts, whereas phloem transports sugar to the plant’s roots.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.