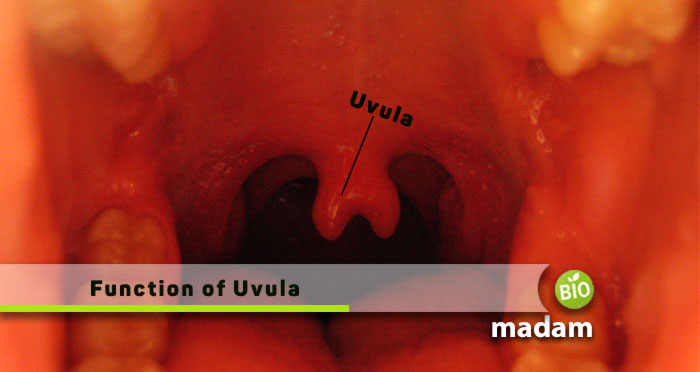
Human anatomy and physiology are quite complex, comprising various organs. However, often we wonder about the reason for a specific body part that apparently seems useless. Uvula is one such tiny organ in the body that hangs at the back of your mouth and looks like it has no significant function. Yet, we must remember that all tissues and organs, including the hair on your body and the uvula in your buccal cavity, have a specific role. This article will tell you everything you need to know about the structure and function of Uvula.
What is Uvula?
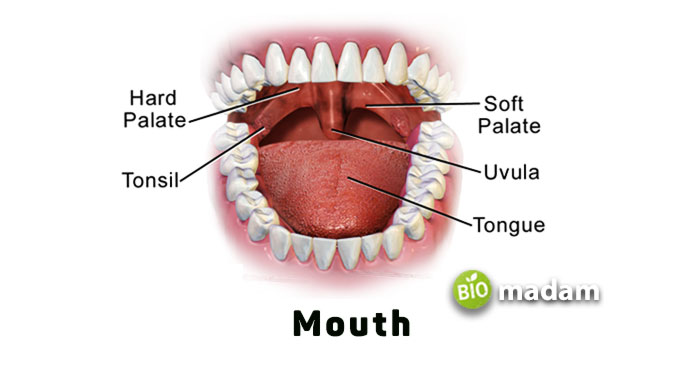
The uvula is a small finger-like or teardrop-shaped tissue that hangs down the soft palate on the roof of your mouth. It is typically pinkish but may vary among red, brown, or purple. It is made of connective tissues and muscles and is covered with a mucous membrane. The same mucous membrane also covers the rest of your mouth, including your teeth and the roof of the mouth.
Commonly known as the uvula, the scientific term for this tissue is Palatine Uvula. So, if someone mentions uvula or the hanging flesh in your mouth, they refer to Palatine Uvula. The musculus uvula within your mouth broadens and shortens the uvula.
Functions of Uvula
Researchers have been trying to find out the exact function of uvula for a long time. Though it is not believed to have a distinct function yet, it acts as an accessory to speech. The palatine Uvula also produces large quantities of saliva in lesser time.
Saliva Production
Saliva is critical to prevent dry mouth and facilitate digestion. Uvula plays a major role in producing saliva as it contains serous and seromucous glandular masses, muscular tissue, and excretory canals. Thus, it enables the organ to produce large quantities of saliva. The research has been strengthened by people who have had their Uvula removed as they mentioned less saliva production in their mouth.
Gag Reflex
The Uvula in your mouth contributes majorly to preventing the entrance of food to the wrong canal. When something that should not go that way touches the Uvula, it induces vomiting and gagging if the food enters another canal instead of the esophagus. It signals that the food is going the wrong way and prevents the entry of food to avoid choking.
Covering the Nasopharynx
The soft palate and uvula move together when swallowing food to shut off the nasopharynx to prevent food from entering the nasal cavity. Thus, when the nasopharynx is properly closed, no food will enter the nasal cavity leading to breathing problems.
Speech Articulation
What might seem apparently useless is vital in producing several sounds in German, French, Arabic, Hebrew, etc. It helps with consonant sounds, also known as the Uvular consonants.
Uvulectomy
Uvulectomy refers to the surgical removal of your uvula due to one or more of the following reasons:
- Your uvula is too long, causing obstructive sleep apnea or snoring
- It sits in front of the throat and blocks your airway
- A swollen Uvula touching the tongue
Removing the Uvula does not involve high risk, as you can live a healthy life without a Uvula, especially when it affects your living standard. Uvulectomy may give you a sore throat for a few days, followed by throat dryness due to less saliva production and difficulty swallowing.
The best approach is to rest for two weeks after the uvulectomy, drink plenty of water, eat soft foods, and take pain relief medication, like analgesics, prescribed by the doctor.
The Bottom Line
The uvula is the flesh hanging on the back of your mouth. It has the shape of a teardrop or small finger. You can see it in the mirror when you open your mouth wide. The uvula is not directly a part of your digestive systems like the stomach or small and large intestine, but it can be considered a part of the GIT. It closes the nasopharynx to ensure the food passes through the esophagus instead of another canal. It plays a significant role in speech articulation and contributes to the gag reflex.
FAQs
Is uvula an organ of speech?
The uvula plays a role in articulating the sound of some consonants, also known as uvular consonants. It contributes to the formation of various sounds in languages like French, German, Arabic, and Hebrew.
What if my uvula is touching my tongue?
Sometimes your uvula becomes swollen and may touch your tongue or throat. The inflammation in the uvula may also affect your speech and voice.
Is it painful to remove uvula?
Uvula is at the end of your mouth, where the food passes to the esophagus. Thus, removing the uvula may seem painful for a few days. You may also experience moderate to a severe sore throat. However, an adequate treatment regimen can reduce the associated pain.
What happens when your uvula is too long?
If your uvula is too long, it may hang lower and touch other parts of your mouth, including the epiglottis, vocal cords, and pharyngeal wall. Irritation in these regions may lead to chronic cough and sleep apnea.
Is uvula hard or soft?
Uvula is a piece of soft tissue hanging from the back of your mouth comprising connective tissues, salivary gland, and muscles.
Why do only humans have uvulas?
Uvula is only present in humans as it differentiates animals from human beings by producing specific sounds. It also produces a large amount of saliva that plays a role in human speech.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.