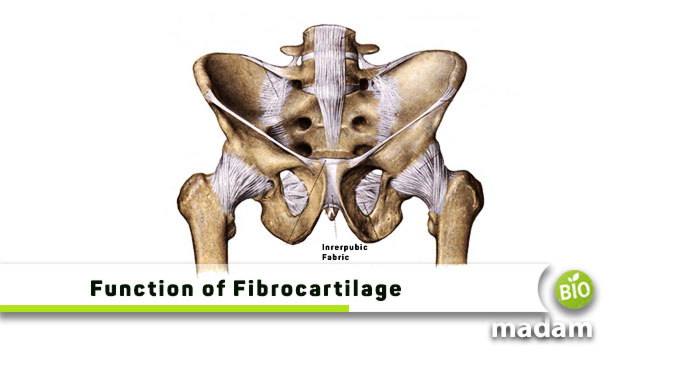
Human anatomy and physiology constitute various tissues and organs contributing to the normal functioning of the body. Besides muscles and bones, connective tissue also plays a critical role in providing structure and movement to the body. The connective tissues in blood, including tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, ensure that the bones and muscles move conveniently. The cartilage of different types performs specific functions, including friction reduction, shock absorbance, and supporting body structure. Fibrocartilage is one of the three types of cartilage in the body. Let’s tell you everything about the specific function of fibrocartilage and other types of cartilage.
What is the Fibrocartilage?
Fibrocartilage is a tough cartilage comprising thick fibers. It is the least flexible and most rigid connective tissue in the body and plays a major role in holding the body parts together. Fibrocartilage also absorbs most of the impact on your bones to protect them.
Fibrocartilage is found in the wrap-around regions where the tendons work with the libs to offer a pulley system for movement. Moreover, they are also seen in the enthesis organs that have increased stress. Thus, you can find fibrocartilage in locations around muscles, tendons, and ligaments for added support. It is also present in the disks between the vertebrae and meniscus in your knee.
Functions of Fibrocartilage
The main functions of fibrocartilage involve providing support and protection against stress and shock. This form of cartilage is present in locations that require additional support, such as the vertebrates of your spinal cord. The functions of fibrocartilage are specific to the type of fibrocartilage.
Types of Fibrocartilage and Their Function
Connecting Fibrocartilage
Connecting fibrocartilage is present in areas with limited movement but added cushioning to protect the organ from damage. It is seen between intervertebral disks.
Circumferential Fibrocartilage
This type of fibrocartilage is present in the glenoid and acetabular labrum to protect the margins of the joints. They do not have a center and look like hollow rings.
Intra-Articular Fibrocartilage
The intra-articular fibrocartilage is prevalent in the joints to help them glide easily. It contributes to smooth extension and flexion by reducing friction between the joints. Their role as thrust pads helps them stabilize joints with easy movements.
Stratiform Fibrocartilage
This fibrocartilage facilitates the gliding of tendons of the tibialis posterior and peroneus longus. It is a thin layer on the bone to minimize friction between the tendon and the bone.
Structure of Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage is considered a transition tissue between fibrous cartilage and hyaline cartilage. It is white and densely arranged. The cartilage structure comprises fibroblasts and chondrocytes. However, the components of the fibrocartilage may vary according to the location and function of the cartilage in that particular area. For example, the structure and role of fibrocartilage in the glenoid region differ from that in the intervertebral discs.
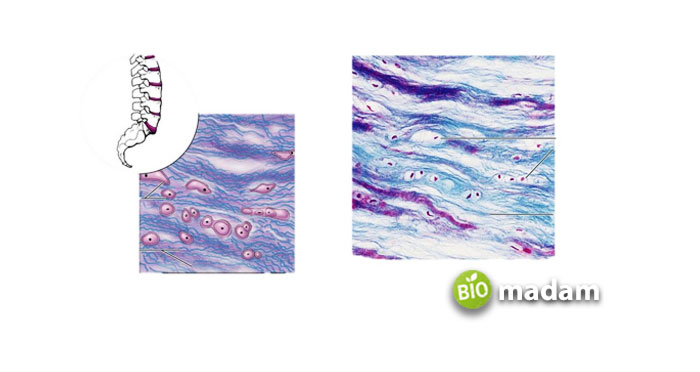
Fibrocartilage-forming fibroblasts and chondrocytes are also referred to as fibro chondrocytes because of their specific development. The cells forming fibrocartilage in the enthesis region have a formation similar to chondrocytes. They have an oval or round shape and lack gap junctions. This characteristic distinguishes fibro chondrocytes from normal osteocytes and fibroblast cells, which have a proper communication system. Fibrochondrocytes contain glycogen and lipids. These components are produced within the endoplasmic reticulum.
Other Types of Cartilage
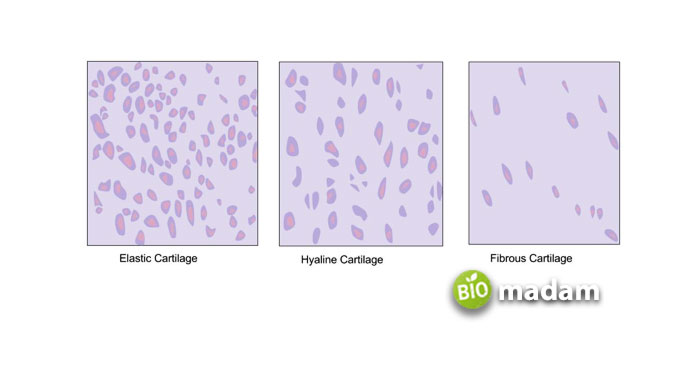
Our body has three cartilage types: fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage, and hyaline cartilage. They are quite similar in composition, making it difficult to differentiate them. However, a few unique features allow researchers to distinguish each cartilage type.
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the most abundant and common type of cartilage in the human body. The main function of the hyaline cartilage is to absorb shock and reduce friction between bones.
Elastic Cartilage
As the name indicates, elastic cartilage is the most elastic and flexible of all three. It has the ability to bounce back to its original shape after enduring strong forces. It may bend without hurting you.
The Bottom Line
Fibrocartilage is one of the three types of cartilage in the body. It is a connective tissue that connects bones and tendons and protects the body from shock. The fibrocartilage in the human body comprises fibrous proteins such as collagen. They are made of fibrocartilage-producing cells, fibro chondrocytes that resemble osteocytes, and fibroblast cells. The functions of fibrocartilage depend on their location and function. The four types of fibrocartilage in the body include connecting fibrocartilage, circumferential fibrocartilage, intra-articular fibrocartilage, and stratiform fibrocartilage.
FAQs
What is a major characteristic of fibrocartilage?
Fibrocartilage is the toughest and least flexible type of cartilage in the body. It is present at the insertions of tendons and ligaments. It is also found in the intervertebral disks of the spinal cord.
What is the functional difference between fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage?
Fibrocartilage and hyaline cartilage are entirely different from each other in terms of strength and flexibility. Fibrocartilage is the strongest, whereas hyaline is the weakest cartilage.
Why is fibrocartilage the strongest cartilage?
Fibrocartilage comprises multiple layers of dense collagen fibers and a hyaline cartilage matrix that gives it a thick look. The collagen fibers are present in the direction of the function stress to prevent damage to bones.
How is fibrocartilage nourished?
Fibrocartilage has no direct blood supply and receives nutrients through osmosis and diffusion, allowing nutrients to enter the chondrocytes. The compressive forces acting on the cartilage enhance the rate of diffusion.
Does fibrocartilage have nerves?
Fibrocartilage does not contain blood vessels or cartilage. Thus, you might not feel any pain associated with pathological conditions of the fibrocartilage. These conditions may arise from inflammation in the surrounding structures.
Is fibrocartilage a bone?
Enthesis fibrocartilage attaches to the epiphyses of the long bones in the ligaments and tendons. It may also have periosteal sesamoid fibrocartilage.
Is fibrocartilage weight-bearing?
The fibrocartilage protects the human knee joint tissues, stabilizing weight-bearing structures. Their rigid structure provides added protection to the bones.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.