Recently updated on March 7th, 2023 at 06:01 am
The respiratory system is a crucial network of tissues and organs as it performs the most critical function of breathing. Breathing may seem like an effortless, everyday action that does not require extra work, but your right and left lungs work hard to ensure efficient breathing. Yet, sometimes, your lungs or airway might not work properly, and you may feel changes in your breathing patterns. Abnormal breathing patterns may indicate an underlying disease due to changes in your body’s anatomy. It could be due to internal changes or external antigens and pathogens. Let’s tell you about the different types of breathing problems and how to manage them.
What are Breathing Problems?
As the name indicates, breathing problems refer to issues while breathing or respiration. They might arise due to an underlying condition and present symptoms like shortness of breath and obstructed breathing. This typically happens when your lungs do not get enough air, and you feel suffocated. Sometimes breathing issues may arise from environmental conditions like higher altitude, physical exercise, or health conditions like asthma.
Breathing problems can be understood by analyzing the respiration rate of the patient. The normal respiration rate for an adult is 12 to 20 breaths per minute on resting. The normal respiration rate may vary with age and physical condition like walking, lying down, working out, etc. If you do not have a medical professional around, you can easily measure your respiration rate by counting the number of breaths you take in a minute.
Types of Breathing Problems
Breathing problems present in the form of respiratory discrepancies. The exhibition of changes in the breathing style may be in different ways. Some people experience higher respiratory rates, while others may observe lesser breaths per minute. Some of the common types of breathing problems include:
Hyperventilation
The “hyper” in hyperventilation indicates an increase in the breathing rate. While taking in oxygen and getting rid of carbon dioxide is important, excess of everything is wrong. Hyperventilation occurs when your body breathes faster and expels a lot more carbon dioxide than required. It disturbs the normal carbon dioxide concentration in your blood. Hyperventilation can make you dizzy and confused as the body fights for the exhalation of carbon dioxide. It may result from an intense workout. Yet, medical conditions like asthma may contribute to it.
The typical treatment of hyperventilation is to breathe into a paper bag instead of open air. Breathing into the paper bag and breathing in will allow you to take in some of the carbon dioxide you breathe out. However, doctors recommend breathing exercises like alternate nostril breathing or pursed lip breathing to limit the inhalation of air and improve breathing.
Dyspnea
Dyspnea is another breathing problem humans face and one of the most common respiratory issues. If you see yourself or anyone saying they are short of breath, it means they are experiencing dyspnea. Dyspnea simply refers to a lesser air intake, affecting the lungs’ normal functioning. It may be due to obesity or being at higher altitudes as well. Dyspnea is not a health condition but a sign or symptom of other underlying health issues. It could indicate lung issues like pulmonary embolism or even a heart attack. If you experience dyspnea frequently, do not let go of it and consult a doctor immediately. Your doctor might give you oxygen or advise another suitable solution.
Dyspnea can be of different types depending on your position and physical condition. Orthopnea is the shortness of breath when you lie down. It is prevalent in people with heart failure. Trepopnea arises when you lie on a particular side, either the left or the right. It typically occurs when lying on one specific side only and not the other. Platypnea occurs in a standing position, and patients feel better lying down. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea is another type of dyspnea associated with sleep. Low oxygen levels lead to difficulty breathing, which wakes you up in the middle of the night. This condition also indicates heart failure.

Hyperpnea
Hyperpnea can be considered the opposite of dyspnea as it leads to an excess of oxygen in your lungs. You experience hyperpnea when taking more air than needed, with or without breathing faster. Like other breathing conditions, it may also arise from a breathing condition that makes it difficult for the lungs to utilize the oxygen entering the body. It may also arise due to an overreaction by your body’s immunity leading to sepsis. Hyperpnea may eventually move to hyperventilation.
Tachypnea
Tachy in medical terms translates to faster. Thus, tachypnea means that you are breathing faster than standard. The number of breaths per minute indicates the condition. People with tachypnea exhibit more breaths than normal due to faster breathing. It may also indicate a lung issue considering the air intake into your lungs. It is common in obese people or children born with lung defects.
Bradypnea
Bradypnea is the opposite of tachypnea and refers to slower breathing than normal. It shows that your body is not getting enough oxygen or cannot inhale properly. Bradypnea may indicate sleep apnea or metabolic issues. At the same time, it may also be a symptom and help in the diagnosis and prognosis understanding of a drug overdose or carbon monoxide poisoning.
Kussmaul Breathing
Kussmaul breathing is also similar to hyperventilation but accompanies deep breaths. This particular type of breathing issue is prevalent in people who have diabetic acidosis due to diabetes. As your body is not able to utilize glucose in the body for bodily functions, it burns stored fat instead and increases acid levels in your blood. Ultimately, the body tries to exhale more carbon dioxide to maintain the normal balance of components in the blood. It pushes the respiratory system to work faster to inhale and exhale more. The deep breaths resulting from this process often smell fruity, known as Kussmaul breathing.
Symptoms of Breathing Problems or Difficulties
While shortness of breath and faster breaths are the most common symptoms of problems like dyspnea, hyperventilation, etc., there is more to it. Pulmonologists mention that people often think being tired is the same as shortness of breath, but it is not the case. It is normal to be out of breath after a strenuous exercise or feel like you are not getting enough air. Relaxing for a while will help you regain the oxygen and feel normal after a few minutes. Contrarily, if you find breathing difficult even when you are resting, you might need to see a doctor.
The symptoms of breathing difficulties may include
- Rapid breathing
- Difficulty to inhale
- Anxiety
- Tachycardia (increased heart rate)
When Should you Consult the Doctor?
If you are short of breath and feel faint or sick, it is best to call an ambulance for medical assistance. However, you must rush to the emergency in case of extra effort for breathing, shortness of breath on lying down, fever, blue lips or fingertips, and hearing sound while breathing.
If you can speak full sentences easily, there is no need to run to the emergency. Moreover, a little fluctuation in breathing is normal with health conditions like asthma or bronchitis. But, if the symptoms are not normal for you, it is concerning, and you should consult a doctor.
Some of the breathing problem signs that require medical attention include:
- It happens more frequently and more severely after physical activity
- It has started to happen recently, and you have not experienced it earlier
- Dyspnea does not go away even when you are lying down
- You experience high fever, cough, or swelling in ankles and feet
- Breathing difficulty is severe and interferes with daily functioning
- It does not go away when sitting or resting
- It may indicate a heart attack when accompanied by chest pain that spreads to your arms, jaw, neck, or back.
- Blue lips or fingertips may also suggest a heart issue
Causes of Breathing Problems
The breathing problems may arise from medical and non-medical issues. Some issues are more widely spread than others that causing breathing issues. Some of the medical causes and risk factors of breathing problems include:
Heart Diseases
Heart diseases can be a risk factor for developing breathing difficulties as the heart cannot pump enough blood to body organs. Thus, the body tries to inhale more oxygen to ensure proper functioning.
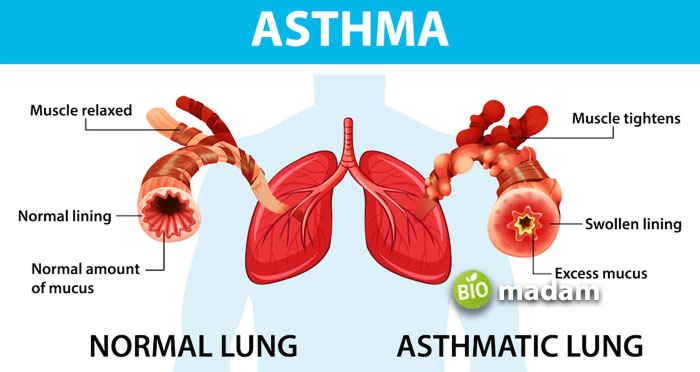
Asthma
Asthma results from inflammation in the airway. Thus the main symptom of asthma is difficulty in breathing.
COPD
COPD conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema make it difficult for the lungs to exhale.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is another lung-related condition that leads to inflammation of the respiratory tract and makes it difficult to breathe. Bacteria or viruses may cause pneumonia.
Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism results from an embolism or blood clot in an artery in the lung that reduces the transfer of oxygen from the lungs to other body parts. It is often linked to heart attack as the blood clotting can even block the passage of blood towards the heart.
Anemia
While anemia is not directly related to breathing issues, it can eventually cause respiration difficulties. Anemia arises from a lack of hemoglobin that works to transport oxygen throughout the body. So, when the body lacks hemoglobin, it affects oxygen transport, and breathing requires more effort.
Flu
Colds and flu can be due to any viral or bacterial infection that are not long-term medical problems but can cause breathing problems. These infections lead to the swelling of the airway and block the movement of oxygen to the lungs.
Allergies
Allergies refer to reactions by the body on exposure to a foreign body that seems harmful to the immune system. Asthma and breathlessness are among the symptoms of allergies caused by animal dander and pollen grains. Sometimes anaphylaxis may lead to blockage in the breathing airway until the allergic reaction clears up.
Anxiety
Anxiety is a medical condition that is observed to affect your physical health. Severe anxiety can result in symptoms like breathing problems, such as hyperventilation, which cause quick breathing. Panic and anxiety may worsen the situation if not managed soon.
Obesity
Obesity also leads to difficulty in respiration if not handled in time. People who especially have extra fat on the neck or thoracic region have a higher chance of difficulty in breathing, causing a disorder known as obesity hypoventilation syndrome.
Inactivity
Inactivity is a less common but important risk factor for breathing problems. When you do not perform any physical activity for a longer time, the heart muscles weaken over time and make breathing difficult.
Medicines
Sometimes medicines may also change your normal body functioning as a side effect. For example, aspirin can cause breathlessness if you already have asthma.
Besides the medical reasons mentioned above, a few environmental factors in our biomes and biospheres may contribute to breathing issues. They include:
Poor Air Quality Index
Due to lifestyle changes, air quality around us is also being affected. Polluted air can irritate the airway and lead to asthma and shortness of breath.
High Altitudes
It is usual for trekkers to experience shortness of breath at higher altitudes due to less oxygen. If you are visiting a high-altitude area for the first time, you might feel uncomfortable and light-headed for a longer time.
How to Prevent Breathing Issues?
Breathing issues can be difficult to manage when not handled in time. You can avoid complications by preventing these issues before they arise or in the early stages. Some of the steps you can take to prevent breathing issues include:
Stay Active and Hydrated
Contrary to popular opinion, working out does not damage your lungs but strengthens them. As mentioned above, longer periods of inactivity also lead to breathing problems. So, adding a workout to your daily routine is recommended to improve your lung function. It also allows you to lose weight if you are overweight. Losing weight will bring you to your ideal weight and save you from breathing problems arising from more fat in the neck and abdominal area. Another way to help you with improved respiration is an adequate water intake. Water intake helps maintain the mucus that keeps your lungs free from external antigens, like exogenous antigens.
Stay Away from Pollutants
You might think it is not realistically possible to avoid pollutants. Yet, you can minimize your exposure to harmful particles in the environment. Smog and pollutants in the lung increase your risk of developing lung diseases and disorders. Moreover, home products like scented candles and cleaning products may also contribute to breathing issues. Wear masks in regions with a high air quality index indicating poor air quality.

Quit Smoking
Tobacco smoking is one of the most common causes of cancer and other problems like breathing problems. It also contributes to COPD. Experts suggest that you will observe a change in your breathing pattern within the first two weeks of avoiding smoking or vaping.
The Bottom Line
Breathing is a natural phenomenon, and people often fail to observe breathing issues due to underlying health issues. Breathing issues are of different types, including hyperventilation, hyperpnea, tachypnea, bradypnea, dyspnea, etc. Sometimes, these issues may be due to workouts or physical movement. You do not have to visit the doctor if you can breathe properly after a couple of minutes. Alternatively, in case you feel breathless when resting or lying down, it is important to consult the doctor. It could be due to environmental factors like smog, high altitude or resulting from a medical condition like asthma or COPD. The physician will advise a suitable treatment according to your condition to improve your breathing.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.