Recently updated on October 30th, 2023 at 09:55 am
Transpiration and evaporation are common phenomena that occurs in our biomes and ecosystems. Evaporation refers to the process of converting a liquid into vapors. On the other hand, transpiration is the release of water from plants in the form of vapors. While the techniques are somehow similar, they are not entirely the same. One major difference between evaporation and transpiration is their environment. Evaporation may occur in different areas, even those that lack plants. However, transpiration is specific to green plants.
Keep reading to learn all the differences between evaporation and transpiration.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Evaporation | Transpiration |
| Definition | Liquid to vapors | Loss of water vapors |
| Process | Physical | Biological |
| Function | Formation of cloud | Helps plants cool |
| Factors | Water presence | Water content in soil |
| Occurrence | Non-living surfaces | Living cells |
| Speed of Process | Fast | Slow |
| Time of Occurrence | Day and night | Day |
| Effect on Surface | Dry | Not dry |
| Uptake of Minerals | Absent | Present |
| Applications | Salt extraction and drying clothes | Transportation of water and nutrient |
What is Evaporation?
Evaporation is the process of conversion of molecules or compounds from liquid to gaseous state. Particularly, evaporation allows water to enter the atmosphere in the form of water vapors for the water cycle. While many pure substances and mixtures may evaporate, it is most abundantly observed in water molecules.
This phenomenon takes place naturally globally in different types of biodiversity containing a water body. The water in lakes, ponds, rivers, oceans, water puddles, and even in soil evaporates to become vapors. The process is energy-driven which is obtained from the sun. Thus, evaporation is an endothermic reaction.
Did you know: one gram of water requires around 600 calories of heat energy to evaporate?

Process of Evaporation
Evaporation involves heat to convert liquid molecules to gasses. Let’s tell you how the process of evaporation takes place.
- When the water (or any liquid) molecules receive energy, they strike each other, and energy transfer occurs.
- The molecules absorb energy from neighboring molecules and try to overcome the pressure.
- At the boiling point, the energy is so high that the molecules escape the container in the form of vapors or gas.
- Eventually, the temperature in the surroundings falls as the loss of vapors reduces the liquid’s temperature.
- After some time, the evaporation rate becomes equal to the condensation rate, and the setting reaches equilibrium.
Factors Affecting Evaporation
Numerous factors in the ecosystem and community of the water body make a difference in the evaporation rate. They may fasten or slow down evaporation according to environmental conditions.
The factors that affect evaporation include:
Temperature
Evaporation is completely dependent on temperature. Fluctuations in temperature make a huge difference in the rate of evaporation. Higher temperatures provide more energy to the molecules. Thus, the rate of evaporation is faster in warm areas.
Pressure
Unlike temperature, the effect of pressure is inversely proportional to the evaporation rate. Less pressure on the surface will lead to a higher evaporation rate.
Intermolecular Force
The bonding between molecules of an element, whether ionic or covalent, also affects how it will react to heat. Stronger intermolecular forces mean a faster transfer of energy and more evaporation.
Surface Area
The surface area of water is directly proportional to the evaporation rate. There are more molecules in a larger surface area which increases the probability of escape of more molecules.
Wind
The wind is not generally considered a critical factor in evaporation, yet it plays a major role. Wind clears up space in the area, enabling more molecules to escape the surface. Thus, faster wind means more evaporation for the day!
Humidity
When the wind speed is low, humidity is high because of a higher number of water vapors. Therefore, higher humidity reduces the rate of evaporation.
Applications of Evaporation
There are numerous applications of evaporation in our daily life. Water vapors leave your clothes by the heat from the sun during sun drying. The preparation of table salt also involves the evaporation of seawater. Researchers separate elements from homogenous and heterogenous mixtures in laboratories through evaporation.
What is Transpiration?
Transpiration is a biological process in which the water loses the surface of plants in the form of vapors.
It is an important process besides photosynthesis and cellular respiration that takes place in all vascular plants, and not in non-vascular. The water vapors leave the surface of aerial parts of plants through tiny openings called stomata.
Transpiration also facilitates the transport of nutrients from the roots to different parts of the plant. It is critical to plants and enables them to survive in severe drought conditions.
Water is essential for plants, yet only 3% to 5% is used for metabolism and growth. The rest of the absorbed water is released into the surroundings through transpiration.
Transpiration may be called a type of evaporation specific to plants.
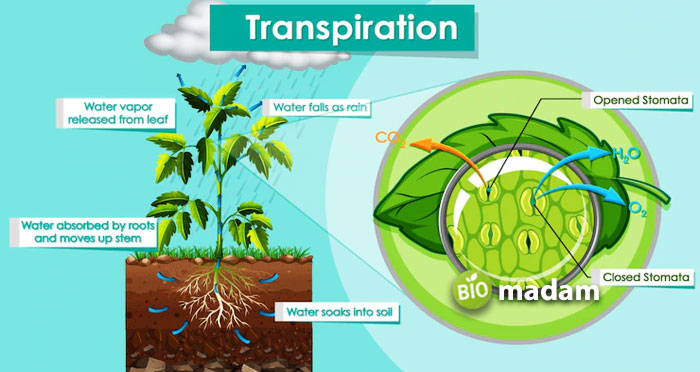
Process of Transpiration
Transpiration occurs through the leaves of the plants as the water evaporates from the leaves. Here is the complete process of respiration:
- The plant roots absorb water from the soil along with nutrients.
- Water and other nutrients travel to parts of the plants where they are required.
- The plant uses the water transported through capillary action for various activities.
- The remaining water evaporates from the surface of the leaves through transpiration.
Factors Affecting Transpiration
Like evaporation, transpiration also depends on a few features that may increase or decrease the speed of transpiration from the plant surface. Some of the factors include:
Temperature
As transpiration is a form of evaporation, the temperature has the same effect on transpiration. Plants transpire more in warm temperatures as more water leaves the surface of the leaves.
Light
More sunlight causes the pores (stomata) on the leaves to open for photosynthesis. Thus, the opening of the stomata leads to transpiration.
Soil Water Content
The water content in soil is a crucial factor in transpiration in plants as it is responsible for providing water to the plant. If the soil does not have enough water to replenish the plant, the stomata do not allow evaporation from leaves.
Number and Size of Leaves
The number and size of leaves are directly proportional to transpiration. Large leaves provide a wider surface area to the leaves for transpiration. Similarly, more leaves also mean a higher loss of water.
Applications of Transpiration
Transpiration is specific to plants and provides water and nutrients to all parts of the plants. It supplies water and nutrients to leaves for photosynthesis. The water needed by the plant regulates the rate of transpiration.
Differences Between Evaporation and Transpiration
Definition
Evaporation
Evaporation refers to the conversion of liquids into gas in the form of vapors.
Transpiration
Transpiration, on the other hand, is the loss of water from the leaves of plants under sunlight.
Process Type
Evaporation
Evaporation is a physical process occurring in different ways around us.
Transpiration
Transpiration is a biological process occurring in only green plants, compared to algae and other organisms.
Function
Evaporation
Evaporation of water contributes to the water cycle through the formation of clouds.
Transpiration
Transpiration helps plants keep themselves cool and avoid burning on hot days.
Depending Factors
Evaporation
Evaporation continues in any environment till the liquid completely dries off the surface.
Transpiration
Transpiration depends on the water content in the soil and the plant itself.
Rate Influential Factors
Evaporation
The rate of evaporation depends on temperature, pressure, surface area, and humidity.
Transpiration
The increase or decrease in the rate of transpiration is determined by the number and surface area of leaves, temperature, sunlight, and water content in the soil.
Occurrence
Evaporation
Evaporation occurs in different types of aqueous and non-aqueous liquids.
Transpiration
Transpiration takes place in plants and involves living cells.
Speed of Process
Evaporation
The rate of evaporation depends on various factors; however, it is comparatively a faster process.
Transpiration
On the contrary, transpiration is a slower process in comparison to evaporation.
Time of Occurrence
Evaporation
Evaporation may take place at any time of the day or night.
Transpiration
In contrast, transpiration typically occurs during day time when stomata open.
Effect on Surface
Evaporation
The surface becomes dry after liquids evaporate in the form of vapors.
Transpiration
The plant surface does not become completely dry despite the loss of moisture.
Mineral Uptake
Evaporation
Evaporation does not contribute to mineral or nutrition uptake in eukaryotic organisms.
Transpiration
In opposite, transpiration facilitates the uptake of the nutrients in eukaryotic green plants.
Applications
Evaporation
Evaporation occurs all around us in our daily life. Drying clothes and obtaining salt from seawater are common utilizations of evaporation.
Transpiration
Transpiration transports nutrients and water from the root to the aerial parts of the plant. It also helps keep the plant cool on hot days.
What is Evapotranspiration?
Evapotranspiration is the combination of evaporation and transpiration. It represents the total loss of water from the soil through transpiration and evaporation.
Transpiration and evaporation are critical to agriculture as they help determine the irrigation required for the crops. Furthermore, they also affect the moisture in the soil. The evapotranspiration rate is determined by the soil type, crop type, temperature, sunlight, and wind. Higher temperatures, more sunlight, and faster wind increase the rate of evapotranspiration.
The Bottom Line
Evaporation and transpiration are critical processes in our habitats and ecosystems. Evaporation takes place in areas with water bodies, whereas transpiration occurs in ecosystems with green plants having chloroplasts and mitochondria. The main difference between evaporation and transpiration is the specificity of transpiration to green plants. The water transpired by plants helps them keep cool and prevents burning. Evaporation and transpiration release water into the environment in the form of vapors to the water cycle.
FAQs
Which is faster evaporation or transpiration?
While both processes result in the loss of water vapors, evaporation is a faster process. On the other hand, transpiration is a biological process and is comparatively slow.
Does humidity increase transpiration?
Opposed to common perception, transpiration does not increase with an increase in humidity. The presence of water in the air makes it difficult for more vapors to adjust.
Why does water evaporate without boiling?
Evaporation results from increased kinetic energy in the water molecules because of the provided heat. The molecules do not require the water to boil to escape the surface.
Does evaporation and transpiration happen at the same time?
Yes, evaporation and transpiration co-occur with no particular differences. The fraction of the solar radiation reaching the soil surface gives the evaporation from the surface.
What happens after evaporation and transpiration?
After evaporation and transpiration, the water vapors move to the air and condense to form clouds. Eventually, they precipitate back into the soil in the form of rain and snow.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.