The field of biology is so vast, there are so many living organisms, from microorganisms to organisms. All these organisms are composed of basic fundamental units called ”cells.” These cells are the building blocks of life. They are responsible for maintaining life and performing all the functions needed by the organisms to survive. Cells are of different shapes and sizes and are specialized to perform their distinct functions. All these cells have unique structures that are involved in different activities.
Some organisms are unicellular whereas others are multicellular. There are two main types of cells based on their structures and functions, these are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, and the organisms are known as prokaryotes and eukaryotes respectively. Both these cells have distinct features. Eukaryotes have a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Now, let’s find out what are prokaryotes, and what structures they have, and explore whether they have organelles.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
These are the earliest discovered cells. Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms lacking a well-defined nucleus and organelles. They are smaller in size than any eukaryotic cells, typical prokaryotic cells range from 0.2- 2 μm in diameter. They exist in different shapes including, spiral, rod, and sphere shapes. Prokaryotes reproduce asexually by binary fission and sexually by conjugation.
Examples of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells are of two types:
- Bacterial Cells
- Archaeal Cells
Do Prokaryotic Cells Have Organelles?
Prokaryotic cells do not have organelles. Cell organelles are specialized to perform specific tasks. Organelles such as chloroplasts, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum are present in eukaryotic cells but they are absent in prokaryotic cells. All the processes are performed inside the cytoplasm of the cell. Cytoskeleton is also absent in these cells. Prokaryotic cells also lack a proper nucleus, and their DNA is in the nucleoid.
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells
The following are some distinct characteristics of prokaryotic cells:
- They do not have a nuclear membrane.
- They lack chloroplast, mitochondria, lysosomes, and Golgi bodies.
- Prokaryotic cells reproduce sexually by conjugation and asexually by binary fission.
- As there are no mitochondria, the plasma membrane acts as the mitochondrial membrane. It contains all the enzymes necessary for respiratory action.
- The cell wall of a prokaryotic cell is composed of carbohydrates and amino acids.
- A single chromosome carries all the genetic material of the cell.
- They lack histone proteins that are present on the eukaryotic chromosomes.
What are the Structural Features of Prokaryotic Cells?
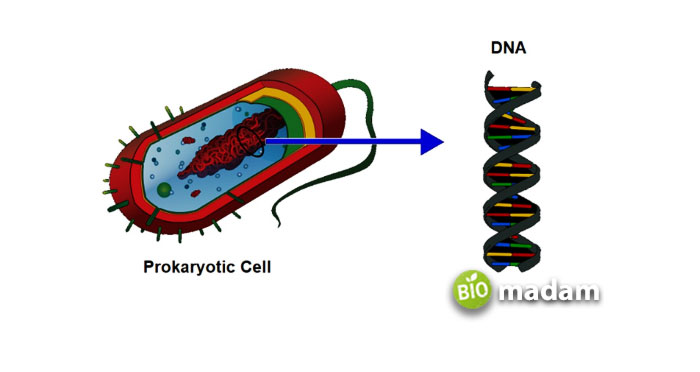
The structures found in prokaryotic cells, along with their features, are mentioned in detail here:
Cell Wall
The cell wall surrounds the cell and gives shape and protection to the cell.
Capsule
In addition to the cell wall, bacterial cells contain a protective covering called the capsule. It protects the cell and plays a role in attachment to nutrients and surfaces.
Cytoplasm
The prokaryotic cell cytoplasm, such as that of bacteria, is a gel-like component containing enzymes, salts, and other organelles.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane covers the cytoplasm and regulates the entry and exit of molecules in the cells.
Pili
These are hair-like outgrowths present on the surface of the cells. They help in attaching to the surface of other bacterial cells.
Flagella
These are long whip-like structures and help in the movement of the cell.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis.
Plasmids
Plasmids are non-chromosomal DNA structures. These structures are not involved in the reproduction process.
Nucleoid Region
The region where the genetic material is present inside the cytoplasm is called the nucleoid region.
Bottom Line
All organisms, whether animals or plants are composed of the basic unit of life. There are two main types of cells, eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Both of them differ depending on their structures and functions. Prokaryotic cells lack these membrane-bound organelles and a proper nucleus is also absent in them. All their functions are performed inside the cytoplasm. The genetic material of prokaryotic cells, unlike eukaryotes, is contained in a nucleoid region present inside the cytoplasm. Bacterial cells and archaeal cells are the two types of prokaryotic cells.
FAQs
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound nuclei and membrane-bound organelles while eukaryotic cells have both.
Which structures are similar between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Several features and structures are similar in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. These include the presence of DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, cell wall, and cell membranes.
Who discovered prokaryotic cells?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hook are two famous microbiologists who discovered prokaryotic cells.
When was the first prokaryotic cell discovered?
The first prokaryotic bacterial cells were discovered 3.5 and 3.4 billion years ago. These cells were photosynthetic, other types of simple bacteria must have existed before this time.
What was the first kingdom for prokaryotes called?
Prokaryotes are placed in Kingdom Monera of the five-kingdom classification system.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.

