Have you ever thought about what would the animal cell look like if there was no cell membrane? There would not be any cells, either! The organelles would not have anything to cover them, and thus the organelles would be dispersed. So, it is not an exaggeration to say that the cell membrane is one of the most critical components in an animal cell besides the nucleus. It is often thought that the only function of the cell wall in eukaryotes is to contain the matters of the cell. However, there is a lot more to the cell membrane than protection.
Let’s tell you about the structure and function of the cell membrane in animal cells.
Cell Membrane in Animal Cell
The cell membrane is the outermost organelle in cells of most eukaryotes and prokaryotes, except for the cell wall in plant cells. The cell membrane acts as a separating factor between the external and internal environment of the cell. It also helps provide a shape to the cell. Though, the rigidity between the cell membrane and cell wall varies, the latter being more robust.
Function of Cell Membrane in Animal Cell
Below are the most prominent functions of cell membrane in an animal cell:
Protection
As animal cells do not have a cell wall, the cell membrane encapsulates the components of the cell. It protects the cell organelles by providing a barrier between the internal and external environment. Thus, it protects the cell’s physical integrity. It also saves the cell from the influence of antigens and pathogens outside the cell.
Transports Molecules
The cell membrane plays a critical role in transporting materials across the cell. It may include the intake of molecules essential for cellular function and the excretion of waste materials.
Prevents Loss of Molecules
Besides transporting molecules in and out of the cell, the cell membrane also prevents the loss of important molecules. It ensures that molecules required for cellular activities do not move out of the cell.
Signal Transmission
The cell membrane contains receptors which communicate with the internal and external environment using biochemicals like neurotransmitters and hormones.
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is also on the list of functions of the cell membrane in an animal cell. It is the process of engulfing molecules within the cell. An invagination forms within the cell membrane or plasma membrane that brings in micro and macromolecules. It requires energy and is thus categorized as an active transport. The process of ingesting liquids is pinocytosis, while solid particle ingestion is phagocytosis.
Structure of Cell Membrane
The cell membrane in animal cells comprises a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are made of two fatty acids combined with a phosphate group. These molecules arrange in a way that they form a bilayer. The head of the phosphate group is hydrophilic, while its tail is hydrophilic. So, the hydrophobic heads of the phospholipid bilayer will stay on the inside when placed in an aqueous solution. At the same time, the hydrophilic heads make contact with water due to their water-loving nature.
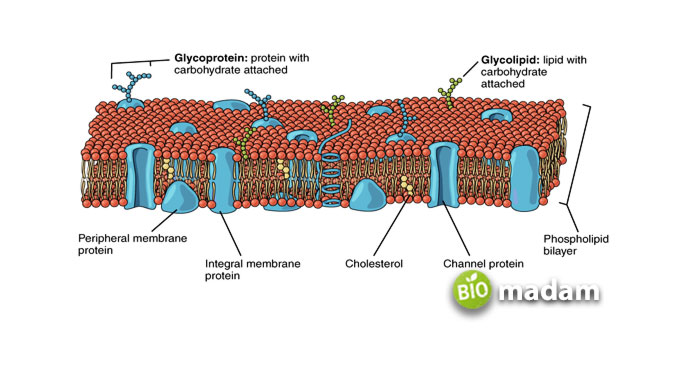
Lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, are present throughout the cell membrane. The cell membrane may comprise 20% to 80% of lipids, depending on its location and function.
Cell Membrane Lipids
The essential lipids existing within a cell membrane are:
Phospholipids
Phospholipids make up the majority of the cell membrane. They form a lipid bilayer with hydrophilic and hydrophobic components. This part of the cell membrane is semi-permeable. It allows the diffusion of only a few particles.
Glycolipids
Besides the attachment of phosphate and proteins, some parts of the cell membrane have glycolipid structures present. These are the carbohydrate molecules joined to the cell membrane and they help recognize and communicate with other cells of the body.
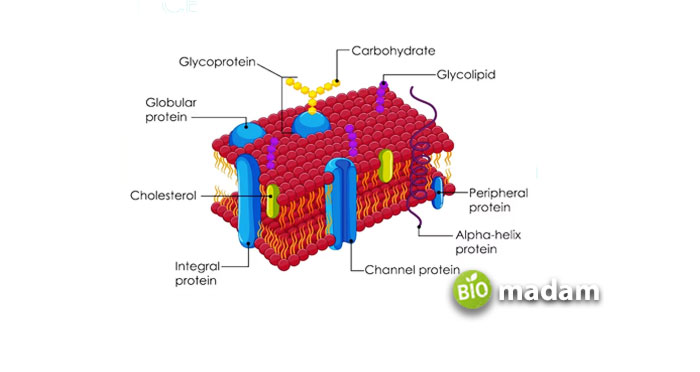
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is another lipid present in the membrane of animal cells. It helps the cell membrane remain flexible by avoiding too close orientation of the phospholipids. Plant cell membranes lack cholesterol.
Cell Membrane Proteins
The most prominent cell membrane proteins are as follow:
Integral Membrane Proteins
The integral membrane proteins are embedded within the membrane and can be seen on both sides.
Peripheral Membrane Proteins
These proteins are not present within the cell membrane but connect to the membrane through interactions with other proteins.
Structural Proteins
Different types of proteins comprising the structural proteins are responsible for providing shape and support to the animal cell.
Receptor Proteins
As the name indicates, receptor proteins act as receptors to carry signals outside of the cell. They use neurotransmitters, hormones and other receptor molecules to pass signals.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with a carbohydrate group attached to them are called glycoproteins. They are also present within the cell membrane and facilitate the transport of molecules.
Transport Proteins
Globular proteins act as transport proteins within and across the cell membrane during facilitated diffusion.
The Bottom Line
Differentiating the internal environment from the external and providing a shape to the cell are the two main functions of the cell membrane in animal cells. It also contributes to the passage of molecules inside and out of the cell to carry on cellular functions. As animal cells do not have a cell wall, it also protects the cell from external antigens like bacteria and viruses. The cell membrane structure comprises a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins and carbohydrates. They facilitate the movement of molecules across the cell and allow communication.
FAQs
Is cell membrane only in animals?
The cell membrane is present in all animal and plant cells. It protects the cells from the external environment and provides a proper shape.
Where is cell membrane animal or plant?
The cell membrane is the outermost layer in animal cells as they lack a cell wall. On the other hand, plants have a cell wall outside of the cell membrane.
Which are present only in animal cells?
Animal cells have lysosomes and centrosomes which are not present in plant cells. Vacuoles in plants carry out the function of excretion of wastes by lysosomes.
What animals have no cells?
All animals comprise cells; however, some organisms, like viruses, viroids, and virions, are non-cellular. Thus, viruses are not considered living organisms either.
How many cell membranes are in an animal cell?
Every animal cell contains only one cell membrane to protect and cover each animal cell. It helps the transport of materials and signals from the cell to others. Solid materials enter the cell through phagocytosis while transport of liquids takes place through pinocytosis.
What are the 3 main molecules of an animal cell membrane?
Animal cell membranes contain a variety of lipids and proteins in their composition. The three main molecules of an animal cell membrane are phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol. It also has proteins that help with the transport of molecules.

Anna has completed her degree in Pharmacy from the University of Hawaii. She is serving as a research assistant in a pharmaceutical company. She had a great interest in writing blogs, traveling to different parts of the US, and trying delicious recipes in her spare time.