Living organisms, whether eukaryotes or prokaryotes comprise various types of cells. These cells have specific organelles, most of which are the same in all. The cell or plasma membrane is one such organelle in all cells. It provides a structure to the cell and distinguishes the internal environment from the external. The plasma membrane comprises carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Membrane proteins are critical to the movement of molecules across the cell membrane, besides other roles.
This article will cover the types of cell membrane proteins and the function of a plasma membrane protein.
Function of a Plasma Membrane Protein
Proteins are an integral part of the plasma membrane, and despite differences in their structure, they collectively contribute to structure and functional roles. Some of the most critical roles of plasma membrane proteins include:
Act as Junctions
Proteins in the plasma membrane connect as tight and gap junctions to join different membrane components and ensure a proper shape. These junctions are also critical for transferring material and communication among proteins.
Anchorage
Membrane proteins perform special functions in a few cells, such as the extracellular matrix and cytoskeleton. The extracellular matrix contains macromolecules such as glycoproteins, enzymes, and fibrous proteins, including collagen. These filaments maintain the cell’s shape and keep the membrane proteins stable.
Act as Enzymes
Proteins and enzymes are present in the plasma membrane and may have an active site on the outside of the lipid bilayer. Thus, these proteins, as enzymes, are then involved in metabolic pathways that provide energy for cellular and biological functions. One of the key functions of enzymatic proteins in the plasma membrane includes the breakdown of lactose into monosaccharides.
Transduction
The presence of membrane proteins across the lipid bilayer allows them to act as receptors and binding sites. They resemble chemical messengers like peptide hormones released by different types of glands within the body.
Cell Recognition
Besides their role in maintaining the structure and function of the cell wall, the function of a plasma membrane protein also involves recognizing cells. Failure to recognize cells can lead to severe infections when antigens and pathogens enter the body. Glycoproteins in the cell membrane are responsible for cell recognition.
Transportation
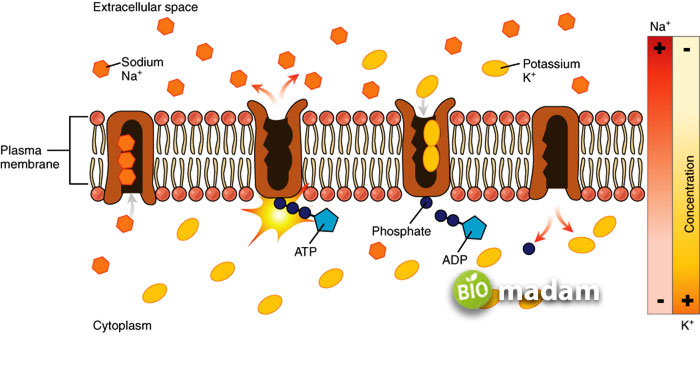
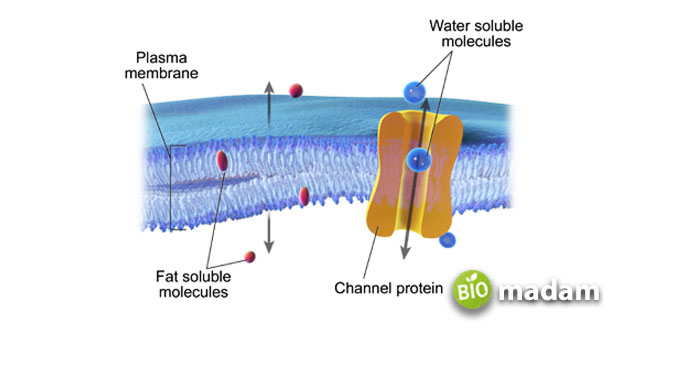
You must have heard of transport proteins in the cell membrane that contributes to the transfer of proteins across the cell. The membrane proteins enable the transport of hydrophilic molecules to pass through the plasma membrane. As protein transport may be active or passive, some of these proteins release ATP as an energy source to move actively.
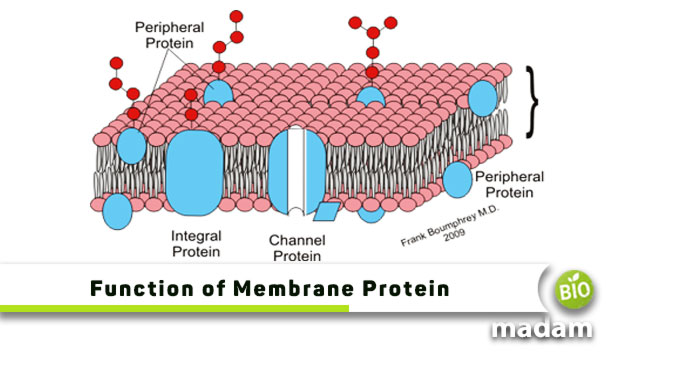
Types of Plasma Membrane Proteins
The plasma membrane comprises two types of proteins within its surface; integral and peripheral proteins.
Integral proteins are attached to the plasma membrane and are present across the lipid bilayer membrane. Their hydrophobic region anchors them to the hydrophobic region of the phospholipid bilayer. The ends of the membrane proteins exposed to the extracellular fluid or cytoplasm are hydrophilic. Some proteins extend through the membrane and may have as many as twelve membrane-spanning sections. These proteins are also known as transmembrane proteins.
Peripheral proteins are attached to the cell membrane on one surface of the membrane through non-covalent interactions with the phospholipids or integral proteins. They are loosely attached and do not join the hydrophobic core of the cell membrane.
The Bottom Line
Different cells in the body form tissues and organs performing specific important functions. The cells comprise a few integral organelles, including the plasma membrane. This important organelle in prokaryotic and different types of eukaryotic cells contains proteins that contribute to the structure and cellular functions. The main function of a plasma membrane protein is to enable the transport of molecules and compounds across the cell. The membrane proteins also play a role in cell recognition, junction, anchorage, transduction, and enzymatic functions.
FAQs
What are the 4 types of membrane proteins?
The four types of membrane proteins include peripheral, integral, auxiliary, and lipid-anchored proteins contributing to structural and functional roles.
What are the common plasma proteins?
Globulin, fibrinogen, and albumin are the most common plasma proteins that help maintain the colloid osmotic pressure necessary for regulating intravascular volume.
What are the five membrane proteins?
The five major plasma membrane proteins include enzymatic, transduction, junction, recognition, and attachment proteins named on their respective functions.
What are the characteristics of membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins anchor cells and ensure your immune system eliminates antigens by recognizing foreign cells.
Is fibrinogen a plasma protein?
Fibrinogen is a critical plasma protein coagulation factor, and a decrease in fibrinogen concentration is associated with a higher risk of bleeding.
What is the main function of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane is the outermost membrane in most eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells except plants and fungi. It gives the cells a shape and contains all the organelles in place. The plasma membrane also distinguishes the external environment from the internal.

Jeannie has achieved her Master’s degree in science and technology and is further pursuing a Ph.D. She desires to provide you the validated knowledge about science, technology, and the environment through writing articles.