What is Biology? Biology is the main branch of science, also known as the science of life. The word biology comprises of two Greek words, “bios” (life) and “logos” (study), and is defined as, “the science of life and living organisms.“
Biological science resides on a vast scale, ranging from the molecular mechanisms in cells, its classification, the behavior of organisms, how species evolve, and extent of its habitat interaction with the ecosystems.
Importance of Biology
The survival of humanity is always a one-million question for humans. Science and biology help identify the issues and present ways to resolve them through scientific research and measures. There are an estimated 8.7 million species on Earth, out of which only 1.9 million have been discovered. Each creation has its impact on the ecosystem. It enables us to make the most of our planet’s natural resources while minimizing their impact on the environment. Biology lets humans be more environment-friendly and save their Mother Nature.

Biology explains forms of life from the unicellular to the most complex multicellular human beings. Different sub-disciplines of biology primarily focus on human health. It studies the origin of diseases, such as the etiology of cancer, infections, and functional problems, and then contrives treatments by using different techniques.
Biology also plays an essential role in the discovery and production of medicines. Moreover, it explains the reproduction process in humans, animals, and plants. Biology helps us recognize animal and plant breeding through several methods. This scientific branch interlinks with agriculture, facilitating us about producing a new and best yield of the plants; that’s why agriculture is establishing day by day.
Human biology focuses on organ and organ systems, including ecology, genetics, physiology, and anatomy. We can increase food production, combat diseases, and save our environment through different biological factors. The advances in this field have resulted in high living standards, attaining food, and appreciating health. Production of plants has been increased by improving the varieties and development of high-yield and disease-resistant varieties, such as plants and animals.
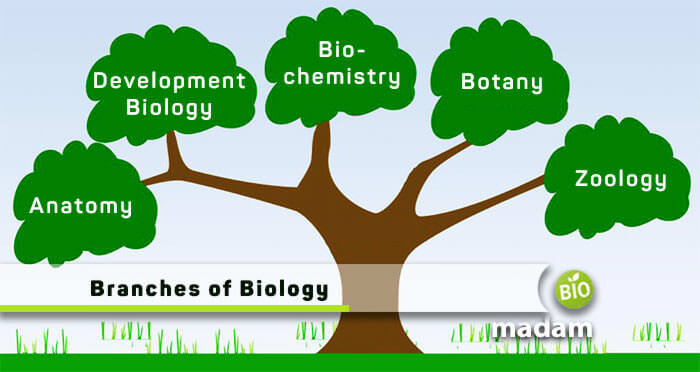
Branches of Biology
There are different branches of biology, and we thought of enlisting the top ten out of all below. These are:
- Anatomy
- Botany and Horticulture
- Zoology
- Biochemistry
- Development Biology
- Cell Biology
- Biotechnology
- Molecular Biology
- Ecology
- Virology
Anatomy
Anatomy comes from a Greek word, “anatomic,” meaning “to cut” or “to dissect.” Information about anatomy gives an extensive understanding of health care. The history of anatomy goes back to two thousand years when it was first discovered around 1600 BC.
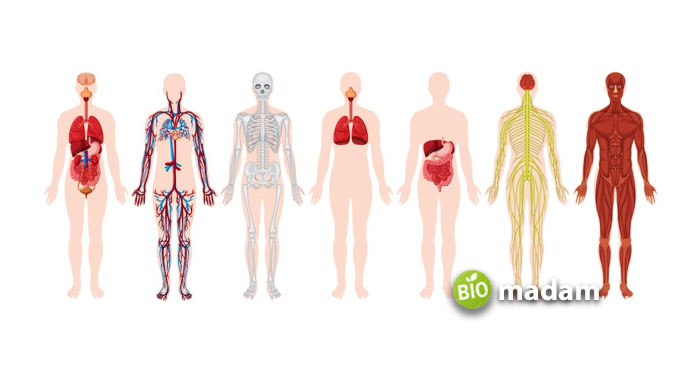
Scientists have further divided it into three fields: human anatomy, animal anatomy, and phytotomy. Human anatomy deals with the study of human organs, whereas phytotomy means studying plant anatomy. We can further explore a living body anatomically in two ways, i.e., Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy and Microscopic Anatomy.
Gross Anatomy
In gross anatomy, biological structures are being studied, which are visible to the naked eye. For this purpose, biologists use different methods, such as endoscopy, MRI, CT Scan, angiography, dissection, and X-ray.
Persons relating to the health care profession, such as dental and medical students, have to dissect part of their practical work in gross human anatomy. Besides this, human corpses are being examined to learn about the major body systems of the human.
Microscopic Anatomy
Histology is another microscopic anatomy, where we study tiny structures of humans, animals, vascular and non-vascular plants, which the naked eye cannot see. The techniques used to study cell and tissue structures are sectioning and staining. These are then observed under a compound microscope.
Career Scope in Anatomy
The ones who specialized in micro-anatomy are known as Histologists. They analyze tissue samples or biopsies taken from the patients to diagnose diseases or infections. Microanatomy is a preliminary study in forensic investigation, which helps explain the reason for the unexpected death of a person.
Archeologists collect biological samples from archeological sites and provide valuable data about the micro and macroevolution of organisms or ancient history.
Histotechnicians or histotechnologists are the experts who prepare slides of affected tissues and add histology stains. These prepared slides are further examined by specialized medical doctors known as pathologists in anatomy.
Anatomy is a major field of specialization in most healthcare-related areas. Paramedics, medical doctors, biological scientists all need training in anatomy.
Botany

Botany is the branch of biology that deals with the scientific study of plant structure, development, life cycle, and their effect on the environment. Botany is studied besides Horticulture, as both are related to plant study. Plants have always been the center of interest for humans due to their valuable and beneficial impact on the climate, weather, and life of humanity. Botany includes the study of:
- Bacteria to algae
- Fungi to algae
- Fungi to lichens
- Mosses to ferns
- Mosses to algae
- Conifers to flowering plants
A person who specializes in botany is known as a botanist.
The plant kingdom is a vast class that is further divided into eight units, including the botany course. Each class has millions of species and subspecies, so this branch of biology provides numerous fields for specialization. Some botanists are interested in studying the interaction of plants with other living organisms and their environment. Others may search to find new species in specific areas or plant growth under different environmental conditions.
Many botanists search about plants’ genetic makeup, the process through which plants convert simple chemical compounds into more complex combinations. The result of these researches has improved our plant production, medicinal food, and fibers. Industrialization caused immense pollution to the environment, so the environmentalists help drain such issues with the association of beneficial plants.
Career Scope in Botany
Research and teaching professions are standard career options for botany graduates. Following are the specialized areas of jobs for advanced botany programs:
- Taxonomist
- Agronomist
- Ecologist
- Mycologist
- Plant Breeder, and
- Horticulturist
The agriculture field demands experienced botanists who can research the methods to enhance cultivation. Furthermore, the government announces jobs in the education, forest, and horticulture department for BS. Botany holders.
Zoology
“Zoo” is a Greek word, meaning animals, and “logy” means study. Zoology deals with the animal structure, genetics, characteristics, classification, behavior, life processes, niches, habitat, and ecological distribution of animals. Animals are a vital part of ecology. Humans from prehistoric times were interested in studying animals, their life cycle, breeding, and their impact on the environment. Zoology has developed as a technology to explore and learn about animals from the micro to the macro level. Submarines powerful cameras, microscopes, and spacecraft helped humans study animals’ lives undersea and in the sky; the life of birds.
This discipline is subdivided into branches, including Ethology, Entomology, Herpetology, Ichthyology, Mammalogy, and Ornithology. Some zoologists study a single animal or an individual category of animals, whereas some examine the anatomy of animals. The zoologists classify their study based on the animals they are observing. For example, mammalogists study mammals, entomologists focus on insects, herpetologists examine reptiles and amphibians, etc.
Career Scope in Zoology
Zoologists have jobs in the teaching department of schools, colleges, universities, health care departments, and teaching hospitals after they graduate in Zoology. Most zookeepers are zoologists. Moreover, the wild animals protection department has specific jobs for a zoologist. In agricultural fields, researchers have a good job scope.
Research is the primary area of zoologists, but no government-funded programs are available for research in zoology.
Biochemistry
Biochemistry is the branch of biology that deals with the biological processes and chemistry of chemical reactions taking place inside an organism. This field helps understand the biochemical phenomenon, such as growth, reproduction, metabolism, heredity, and chemical reactions in a living body.
Biochemists study biomolecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. They are responsible for studying biological molecules’ structure, physical and chemical properties, their interaction with enzymes, and their effect on metabolism. Genetics, enzymology, immunology, cell biology, and plant biochemistry are studied in a biochemistry course.
The essential domain of biochemists is research and analysis of the information collected through different research tools and techniques. Basic techniques which are involved are PCR, Chromatography principles, Gel electrophoresis, etc.
Biochemistry Degree, Career and Scope
After completing the master’s degree in biochemistry, you can specialize in molecular biology, genetics, bioinformatics, development and disease, plant biology, etc. Public and private sectors like medical agriculture, medical instrument companies, research companies and laboratories, and chemical manufacturing companies have specific jobs for biochemists. Cancer research institutes, industrial laboratories, and public health laboratories have specialized jobs for biochemist graduates. The job profiles are biotechnologists, research scientists, research associates, microbiologists, pharmacists, and laboratory technicians.
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the growth and developmental stages of living organisms. In this modern era, genetic control of cell growth, differentiation, and morphogenesis is the primary focus of research and study of developmental biology.
This branch is further subdivided into embryology and gerontology. In embryology, scientists study the initial stages of a developing cell (generally, zygote). On the other hand, in gerontology, we examine physical, mental, and social aspects of a human’s life till aging.
Developmental Biology is an essential discipline in the life sciences. It studies fertility, causes of infertility, human diseases, disabilities, food sustainability, and biological responses to environmental pollution and global warming.
Career Scope in Developmental Biology
Options for a biologist in choosing developmental biology as a career are researcher, cell biologist, and professor. Medical, biotechnology, and pharmaceutical industries also have jobs for developmental biologists. Besides, the government and public health departments hire researchers and research assistants in labs. Nowadays, graduate colleges and teaching hospitals designated a few posts for developmental biologist professors.
Cell Biology
It is an essential branch of biology that studies cell makeup, function, and structure, a process involved in the cell. We know that cell is the primary and fundamental unit of life, containing different organelles. The most prominent are Cytoplasm, Lysosomes, Vacuoles, Golgi bodies, Ribosomes, Smooth & Rough ER, Mitochondria, and many more. All life cycles are performing their function in the cell. They are not clearly seen under a compound microscope instead of electron microscope for detailed study.
Organisms are divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The former has a single-compartment unit, whereas the latter consists of more than one cell.
Biotechnology

This branch is interlinked with other scientific fields, such as genetics, molecular biology, and other similar units. Biotechnology helps enhance our lives and improves nature through different cellular and molecular processes. We have been utilizing biotechnology for many years now to form food products like cheese and bread. Furthermore, biotechnology has helped us fight against deadly diseases, reduced environmental issues, produced energy, feed the hungry, and developed highly efficient manufacturing procedures for industries.
Career Scope in Biotechnology
A biotechnologist can apply in numerous biofields, including manufacturing industries, scientific laboratories, and even a university professors. We are currently utilizing techniques from biotechnology in areas like food processing, agriculture, energy production, and bioremediation. In the forensic lab, lab technicians are performing recombinant DNA technologies and PCR tests with the help of biotechnology. Not only this, but biotechnology made it possible for us to form different medications, for example, different types of insulin. A student can conveniently choose to graduate in biotechnology as it guarantees a successful future.
Molecular Biology

Another prominent branch of biology is molecular biology, but many question, “What is molecular biology?” The branch that relates to examining chemical structures and biological processes of basic units of life (molecules) is called molecular biology. The field mainly concentrates on essential proteins and nucleic acid units (DNA and RNA). It helps us understand how these molecules process, interacts, and interlink with other cells. Although considerably different, molecular biology links with biochemistry, genetics, and biophysics as well.
Career Scope in Molecular Biology
This field hasn’t emerged as a vast career till now, but it’s improving and increasing day by day. If one thinks to choose molecular biology as his profession, he will get the rewards soon. Students who are interested in becoming molecular biologists can enter research labs. A molecular biologist can take part in producing therapeutic drugs and work on them in research centers.
Ecology
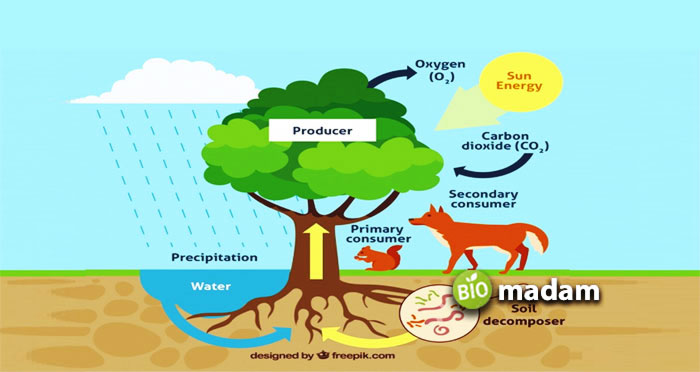
The branch of biology that studies the interactions of human beings with their environment is called ecology. Ecology is divided into many types by ecologists. An ecologist works in four significant organizational levels: organism level, population level, community, and ecosystem. We study the simple communication of organisms with their surrounding at the organism level. Similarly, at the population level, the study extends to observing interactions of one population with other species.
Career Scope in Ecology
An ecologist studies the ecosystem, its biotic and abiotic factors, and how they interact. These include the interaction of human beings with environmental factors, water, air, soil, etc. A person studying ecology can take it to various levels, from examining smaller protein units in biochemistry to analyzing organisms in zoology and botany. It directly impacts scientific branches like geography, geology, chemistry, and meteorology, being an immense field.
Virology

The study of viruses is called virology, which includes examining parasitic organisms and other virus-like entities. When studying these living bodies in detail, a virologist focuses on their life, classification, structure, evolution, and methods of infecting a host cell. To know, how long can a virus live on surface, click here.
Career Scope in Virology
Nowadays, virologists are very important to public health with the increase in viral diseases in the environment. A virologist works to make the best health policies at the local, state, or national level. If you want to become a virologist, you should at least fetch a bachelor’s degree. To further pursue it on a broader level, enroll yourself in a master’s and Ph.D. degree.
Our government is concentrating more on hiring virologists in the upcoming years to prevent the arousal of deadly diseases before their emergence.
What Can You Do With a Biology Degree?
A biology degree opens up a wide range of career opportunities. Some of the top options include working in healthcare, research, education, environmental science, forensics, and policymaking. Those with a biology background are well-suited for roles as doctors, nurses, dentists, pharmacists, researchers, professors, wildlife biologists, ecologists, conservationists, crime lab analysts, science advisers, and more. Biology graduates can also work in hospitals, clinics, labs, zoos, nature preserves, classrooms, and government.
Their expertise allows them to directly help patients and they better understand life on Earth in all its complexity. It wouldn’t be wrong to say that the possibilities are vast for applying biological knowledge to benefit people, animals, plants, and the planet.
Wrapping Up
All in all, the field of biology studies all living things, from tiny cells to entire ecosystems. It covers a wide range of topics like how life begins, grows, functions, and evolves. Biologists use their knowledge to improve healthcare, technology, the environment, food production, and human well-being. They explore new ideas and pass on scientific knowledge to future generations. Even though people have been studying life for a long time, biologists are still discovering new things and finding ways to help society and the Earth.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.

Clear answers
I am student in Grade 12