Evolution is a word well-known to everyone interested in studying and understanding different types of ecosystems. The biomes and ecosystems we live in today are a result of hundreds and thousands of years of evolution. Darwin’s theory of evolution is based on the differential survival of organisms, also called survival of the fittest. Eventually, the fight for survival gave rise to modifications and adaptations in the ecosystems at different levels – macro and micro. Keep reading to learn the differences between microevolution and macroevolution.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Microevolution | Macroevolution |
| Type of Evolution | Intraspecific | Interspecific |
| Period | Shorter | Longer |
| Contributing Factors | Mutation, gene flow/migration, genetic drift, and selection | Microevolution |
| Gene Pool | Rearrangement/modification | Mutations (addition & deletion) |
| Analysis | Mathematical equation | Fossils |
| Examples | New strains of viruses | Vestigial organs, new phyla |
What is Microevolution?
Microevolution refers to the change in species or population over a period. It is attributed to the changes in DNA, genes, and alleles in a population. The combination of genetic material among the members of a group of organisms leads to this kind of evolution. Microevolution takes place over a shorter time compared to macroevolution. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium has proven substantial in the understanding of microevolution in a species.
Genetic mutations or modifications may take place due to genetic drift, gene flow, natural or artificial selection, etc.
A mutation is a change in the DNA or gene sequence of a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell. These changes depict the phenotype gradually in multiple organisms of the same species. The changes in DNA arise from alterations in protein structure. A mutation may occur from different underlying reasons, such as errors in DNA replication, chemicals, radiation, antigens, and pathogens.
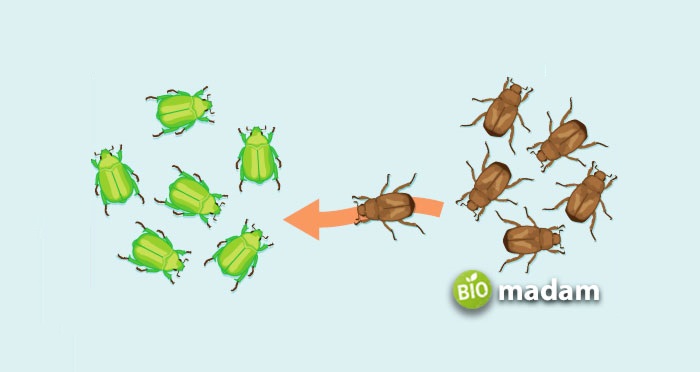
Gene flow and genetic drift are other gene-related causes of microevolution in different species. Gene flow is the movement of genes among organisms when they migrate to different habitats and ecosystems. It leads to genetic diversity within the population. On the other hand, genetic drift in smaller populations results from allele frequency alteration. A natural calamity could be the reason for genetic drift.
The most fundamental cause of microevolution understood by scientist is natural selection. Selection refers to the preferred survival and reproduction of some organisms due to their adaptability and strength. Natural selection leads to genotype and phenotype mutations from one generation to another naturally. Alternatively, artificial selection is a human-crafted method to produce hybrids of different species. It helps the next generation attain good characteristics of both.
Microevolution does not only impact one species. Different types of biodiversity involved in the food chain and food web alter accordingly, making way for microevolution.
What is Macroevolution?
As the name suggests, this kind of evolution occurs at the macro level. Macroevolution refers to big-scale changes that may be easily visible to everyone. Macroevolution may exhibit in developing new organs. These changes are above the species level and may exhibit in various communities and ecosystems.
However, macroevolution takes millions of years to produce changes in populations and communities. It is typically studied through the examination of fossils by archeologists. Discovering this type of evolution allows researchers to understand the speed of changes in organisms’ structure over time. The evolution of monocot and dicot flowering plants is an example of macroevolution.
Researchers view macroevolution through different lenses, including morphological, molecular, taxonomic, and ecological evolution.
Molecular evolution is the most basic level of macroevolution. It refers to the changes in the gene or molecules in the cell. Eventually, the genomic changes may lead to changes in the organism’s anatomy, studied under morphological evolution.
Besides these two levels of evolution, it is also understood as taxonomic and ecological evolution. As the changes in the gene pool of species may give rise to new individuals, it impacts the taxonomic level. Thus, ecologists can examine these changes’ effects on the ecological landscape. It may alter different types of ecology and the behavior of organisms living in a particular habitat.

Similarities Between Microevolution and Macroevolution
- They both are the types of evolution.
- Microevolution and macroevolution show the changes in different ecosystems over time.
- They depend on mutation, genetic drift, migration, and natural and artificial selection.
Differences Between Microevolution and Macroevolution
Definition
Microevolution
Microevolution refers to the changes in the gene pool leading to evolution at the species level.
Macroevolution
In contrast, macroevolution is the set of changes in organisms beyond the species level.
Period
Microevolution
Microevolution takes over hundreds and thousands of years through a few generations.
Macroevolution
Alternatively, macroevolution takes more time than microevolution and may span millions of years.
Level of Evolution
Microevolution
Microevolution falls in the intraspecific level.
Macroevolution
On the contrary, macroevolution takes place at an interspecific level.
Contributing Factors
Microevolution
Mutation, gene flow or migration, genetic drift, and natural or artificial selection lead to microevolution.
Macroevolution
At the same time, macroevolution takes place due to extensive microevolution in the ecosystem.
Genetic Information
Microevolution
Microevolution results from the rearrangement or modification of genetic information.
Macroevolution
Conversely, the mutations (addition and deletion) in genetic information over a large period lead to the formation of new species.
Analysis
Microevolution
The changes due to microevolution may not be visible to a casual observer and are understood mathematically.
Macroevolution
Macroevolution takes place at a broader level and is observed by archeologists through fossils.
Examples
Microevolution
Examples of microevolution include the introduction of new strains of the flu virus and smaller insects.
Macroevolution
The formation of different phyla over time and vestigial organs are examples of macroevolution.
The Bottom Line
Understanding evolution is critical to analyze the relationship between different organisms on Earth. It also helps us understand the changes in our surroundings over millions of years. Macroevolution and microevolution allow researchers to study these changes at different ecological levels. The main difference between microevolution and macroevolution is the period over which they take place. Macroevolution takes millions of years to show results, while microevolution spans a comparatively shorter period. Microevolution leads to macroevolution, giving rise to new species and subspecies.
FAQs
What is example of macroevolution?
One of the most common examples of macroevolution is the origin of complicated organ and organ system structure in mammals.
What is an example of microevolution?
Microevolution occurs at a smaller level compared to macroevolution. The resistance of molecules to DDT is a typical example of microevolution.
What are three types of macroevolution?
The types and patterns of macroevolution include adaptive radiation, coevolution, convergent evolution, and mass extinction.

Hello, I would like to introduce myself to you! I am Chelsea Rogers, an experienced blog writer for science articles, holding an MPhil degree. My enthusiasm to grab the best knowledge, let it relate to botany, zoology, or any other science branch. Read my articles & let me wait for your words s in the comment section.